
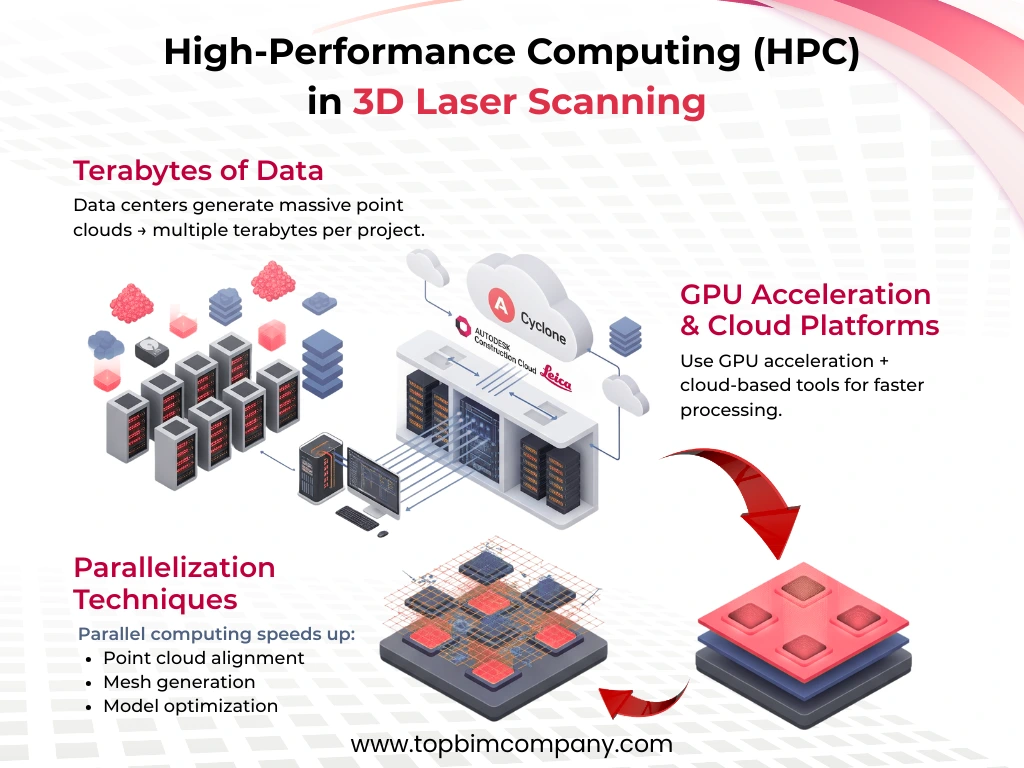
3D laser scanning technology has changed the way we design, build, and manage data centers. This technology captures millions of data points with high precision and creates detailed digital representations of physical spaces. LiDAR technology achieves millimeter-level accuracy (0.5-10mm), which lets data center teams connect physical structures with digital workflows in ways that were impossible before.
Table of Contents
ToggleHow 3D Laser Scanning and Scan-to-BIM Improve Data Center Design
Laser scanning’s precision brings huge benefits to the design phase.
- Scan-to-BIM technology turns raw point cloud data into detailed building information models that are the foundations for renovation and expansion projects.
- Teams can spot hundreds of potential conflicts between systems before construction starts – like ductwork crossing cable trays or piping conflicts with structural beams.
- An international retail group asked Project Surveyors to create a survey-accurate architectural and structural Revit BIM model within 90 days. The precise scanning data helped them finish this massive project on time without compromising accuracy.
Using Digital Twins and 3D Scanning for Data Center Asset Management
3D scanning creates “digital twins” that get continuous updates from sensors and building management systems.
- These virtual replicas give facility managers clear visibility into operational performance without visiting the site.
- Industry experts say this scanning approach reduces measuring time by 60% and modeling time by 40% compared to older methods.
- Facility management teams now merge these scans with Computer Aided Facilities Management (CAFM) software to plan maintenance schedules and track equipment lifecycles better.
Optimizing Data Center Capacity Planning with Laser Scanning
Space optimization remains the biggest problem in data centers.
- Laser scanning helps managers make smart decisions about equipment placement and cooling systems using real spatial data instead of old information.
- Managers can use every square inch better, which improves operational efficiency and cuts costs.
- The technology supports staged implementation strategies for data centers that must stay operational during updates.
- Managers can test different scenarios through digital simulation before making physical changes.
Choosing the Right 3D Scanning Hardware for Data Centers
Specification | Stationary LiDAR (e.g.,Leica ScanStation P40 / P30)
| Mobile SLAM (e.g., Leica BLK2GO)
| Drone-Based Scanning
|
Range | Up to ~350m | 20–100m (indoor navigation) | 50–200m depending on drone + sensor |
Accuracy | ±1–2mm (high precision) | ±10–30mm (less precise) | ±20–50mm (depending on conditions) |
Scan Speed | ~1M points/sec | Continuous while moving | 100k–500k points/sec |
Environmental Tolerance | Works best in stable, controlled indoor conditions | Handles moving through tight spaces, moderate lighting issues | Sensitive to wind, weather, GPS signal, reflections |
Best Use Case | Indoor racks, equipment alignment, piping & structural detail | Complex piping, underground utilities, quick walk-through scans | Exterior utilities, rooftops, large site mapping |
Why Accuracy Matters in Mission-Critical Environments?
Precision in mission-critical data centers isn’t just a technical preference. It’s an operational necessity. Laser scanner accuracy affects every aspect of facility performance and reliability.
How Accurate Laser Scanning Protects Uptime, Safety, and Costs
Data center uptime depends on precise 3D laser scanning. Small inaccuracies in spatial measurements can trigger catastrophic failures when teams install new equipment or modify existing infrastructure. A few millimeters of error might cause cooling problems and create costly downtime through cascading failures.
- Accurate laser scan data helps operators maintain proper clearances around electrical equipment. The data identifies potential hazards before incidents occur. This proactive strategy helps data centers comply with strict safety regulations while protecting staff and critical assets.
- The financial stakes couldn’t be higher. Teams that check laser scanner accuracy before starting projects avoid expensive rework cycles. Precise measurements ensure equipment fits correctly and installation stays on schedule. The result is improved operational efficiency.
- Quality laser scanning surveys create a reliable digital foundation for future planning. This accuracy becomes valuable during expansions or renovations. Teams must work within tight physical constraints without disrupting operations. The original investment in precision gives substantial long-term returns through reduced operational risks and better performance.
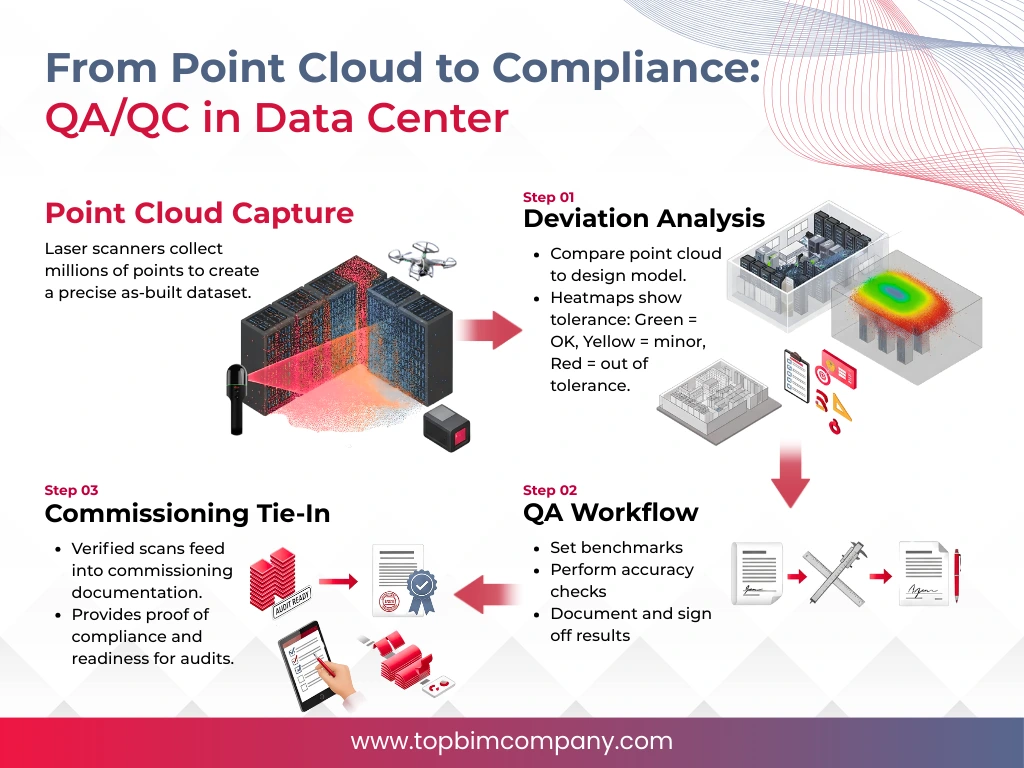
How to Ensure Compliance with Industry Standards?
Data centers must follow industry frameworks that control facility operations and documentation. 3D laser scanning creates detailed digital models that help meet these requirements.
Uptime Institute, ASHRAE, and Regulatory Standards for Data Centers
The Uptime Institute leads the way in validating data center performance through their Tier Certification system. They are the only licensed provider of these certifications. Their assessments make sure the infrastructure has no weak spots and meets global accountability standards. The framework has become a way to measure data center excellence with over 2,800 Tier Certifications issued in 114 countries.
- ASHRAE guidelines play a vital role in thermal and energy performance. Their Standard 90.4-2022 provides detailed requirements for data centers with floor areas that exceed 20 W/ft² and IT equipment loads above 10 kW. ASHRAE also suggests precise temperature control. The inlet air should stay between 18°C and 27°C for the best operation.
- Data centers must also follow broader regulatory frameworks. These include HIPAA, PCI DSS, and regional data protection laws like GDPR in Europe or CCPA in the United States. The precision of laser scan data is a big deal as it helps prove compliance during audits.
- 3D laser scanning at its best creates detailed digital documentation that helps prove compliance. These models give solid evidence that facilities meet required specifications through accurate spatial mapping and inventory tracking. This makes the certification process smoother.
What Mistakes Commonly Happen in Data Center Laser Scanning?
Data center laser scanning projects still face avoidable pitfalls despite today’s advanced technology. Facility managers and scanning technicians can deliver better results by learning from these common mistakes.
Scanning Errors: Incomplete Data, Misalignment, and Setup Issues
- Incomplete data remains the biggest problem in data center scanning projects. Hidden areas behind equipment or overhead infrastructure often go uncaptured, which leaves dangerous gaps in the final model. Dense server configurations create shadow zones that block the scanner’s line of sight.
- Misalignment issues show up when teams try to combine multiple scans into one cohesive model. The resulting point cloud may have overlapping or disconnected sections without proper reference points between scans. This accuracy problem gets worse in larger facilities that need many scanning positions.
- Poor setup choices hurt scanning quality significantly. Wrong scanner placement, rushed calibration, or incorrect resolution settings can make entire datasets worthless. On top of that, active equipment vibration, temperature changes, or reflective surfaces can throw off measurements.
Teams make several other mistakes that come off the top of my head. Poor planning before scan sessions, equipment movement oversight, and inconsistent lighting conditions all play a role. These errors don’t just reduce data center laser scanning accuracy – they lead to rescans that get pricey and delay critical infrastructure projects.
How to Avoid These Mistakes and Guarantee Quality?
Data center laser scanning quality depends on systematic approaches that catch problems before they affect project results. Teams can improve scanner accuracy by a lot and cut down on rework that can get pricey when they use proven methods.
Best Practices to Improve Laser Scanning Accuracy in Data Centers
Detailed pre-scanning protocols set clear goals and boundaries.
- Teams should create scanning schedules during quiet periods and find the best scanner positions to reduce shadow zones. A full picture of existing conditions helps teams spot potential interference points before scanning begins.
- Scanner positions should overlap by at least 30% to curb incomplete data issues. Teams need to use systematic grid patterns when they scan complex environments. Good lighting and removal of temporary obstacles ensure consistent data quality across the facility.
Why Vendor Expertise Matters in Data Center Laser Scanning?
The right scanning partners make a big difference in project success.
- Look for specialists who know data centers instead of general scanning providers. The best vendors should show their previous work in mission-critical environments and understand data center limitations.
- Check if technicians have formal certifications to operate laser scanning equipment and use point cloud processing software. Getting sample deliverables from previous data center projects helps assess a vendor’s eye for detail before you commit.
The Role of Calibration in Accurate 3D Laser Scanning
Precise calibration forms the foundations of accurate scan data.
- Regular equipment upkeep based on manufacturer guidelines prevents measurement accuracy from drifting. Equipment checks must confirm calibration status before each scanning session.
- Temperature, humidity, and vibration can affect laser scanner accuracy.
- Controlled protocols help alleviate these variables. Successful data center scanning projects strike the right balance between technical precision and practical strategies.
Start building a sustainable future today. Get free 3D Laser Scanning consultation for your project.
Case Studies of Successful Data Center Scanning Projects
Organizations across the globe have seen amazing results from using 3D laser scanning in their data centers.
Quail Ridge Data Center, Virginia
The Quail Ridge Data Center in Loudoun County, Virginia, is one of the largest hyperscale facilities in the United States, spanning over 2.4 million square feet.
- During its construction, advanced scan-to-BIM workflows were implemented to ensure precision and efficiency.
- By adopting 3D modeling and laser scanning, the project achieved 99% accuracy in shop drawings and reduced rework by nearly 30%.
- The ability to coordinate mechanical, electrical, and plumbing (MEP) systems in a highly complex environment proved invaluable, ensuring seamless integration of critical infrastructure while minimizing costly field conflicts.
Novva Data Center, Utah
The Novva Data Center campus in Utah, a 1.5 million+ square-foot facility, is another prime example of how large-scale projects benefit from BIM and 3D laser scanning.
- Engineers used digital coordination of underfloor cooling systems and piping to prevent installation conflicts and optimize space utilization.
- Through laser scanning and BIM-driven design, the project team reduced on-site welding, improved installation timelines, and cut costs, all while ensuring uninterrupted operations in this mission-critical environment.
Conclusion
3D laser scanning in data centers is not just about capturing spaces more accurately — it represents a shift in how mission-critical facilities are planned, validated, and operated. The technology bridges the gap between physical infrastructure and digital workflows, giving operators the ability to make data-driven decisions at every stage of the lifecycle.
For owners and operators, investing in accurate scanning isn’t a one-time project cost — it’s a foundation for resilience, efficiency, and competitiveness in a sector where downtime has million-dollar consequences.
In essence, 3D laser scanning transforms data centers from static facilities into living digital ecosystems that can adapt, scale, and prove compliance with confidence. The future of mission-critical infrastructure will belong to those who master this bridge between precision engineering and digital intelligence.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs):
1. What is 3D laser scanning in data centers?
3D laser scanning uses LiDAR technology to capture millions of spatial data points and generate precise digital representations of physical data center spaces.
2. Why is accuracy so important in mission-critical data centers?
Even a few millimeters of error can cause cooling inefficiencies, safety hazards, or equipment misfits, leading to costly downtime and compliance issues.
3. How does scan-to-BIM improve data center design?
Scan-to-BIM converts raw point cloud data into detailed Building Information Models (BIM), enabling clash detection, better coordination, and smoother renovation or expansion.
4. What role do digital twins play in data center management?
Digital twins provide real-time, sensor-linked models of data centers, helping managers optimize maintenance, monitor equipment performance, and plan upgrades without physical site visits.
5. How does 3D laser scanning optimize data center capacity planning?
It helps maximize space utilization, simulate different equipment layouts, and plan cooling strategies efficiently, reducing operational costs.
6. What types of 3D scanning hardware are used in data centers?
Stationary LiDAR for high-precision indoor detail
Mobile SLAM scanners for complex layouts and quick walk-throughs
Drone-based scanners for rooftops, exteriors, and large sites
7. How does laser scanning help with compliance in data centers?
Accurate scans create digital documentation that supports certifications like Uptime Institute Tiers, ASHRAE standards, HIPAA, PCI DSS, GDPR, and other regulatory requirements.
8. What common mistakes occur in data center laser scanning?
Mistakes include incomplete data capture, misalignment of scans, poor scanner placement, rushed calibration, and environmental interferences like vibrations or reflective surfaces.
9. How can teams ensure high-quality laser scanning results?
By following best practices such as overlapping scans by 30%, scanning during quiet periods, using systematic grid patterns, ensuring good lighting, and hiring certified scanning experts.
10. What are the long-term benefits of 3D laser scanning in data centers?
It reduces rework, improves safety, ensures compliance, supports future expansion, lowers operational costs, and strengthens overall data center resilience.
Further Reading
How to Process Laser Scan Data and Select the Right Scanning Provider or Technology?
Ultimate Guide to 3D Laser Scanning & LiDAR Scanning
Comprehensive Guide on As-Built Surveys
How to Conduct 3D Laser Scanning in Data Centers and Choose the Right Tools?
How to Use As-Built Surveys in Renovation Projects and Avoid Common Mistakes?
How to Conduct an As-Built Survey and Choose the Right Tools for Your Project?
Our Services
Latest Post
Get A Free Quote
BIM Construction is the Future
Building information modeling (BIM) is the future of building design and construction. Get in touch with our BIM Experts.





