
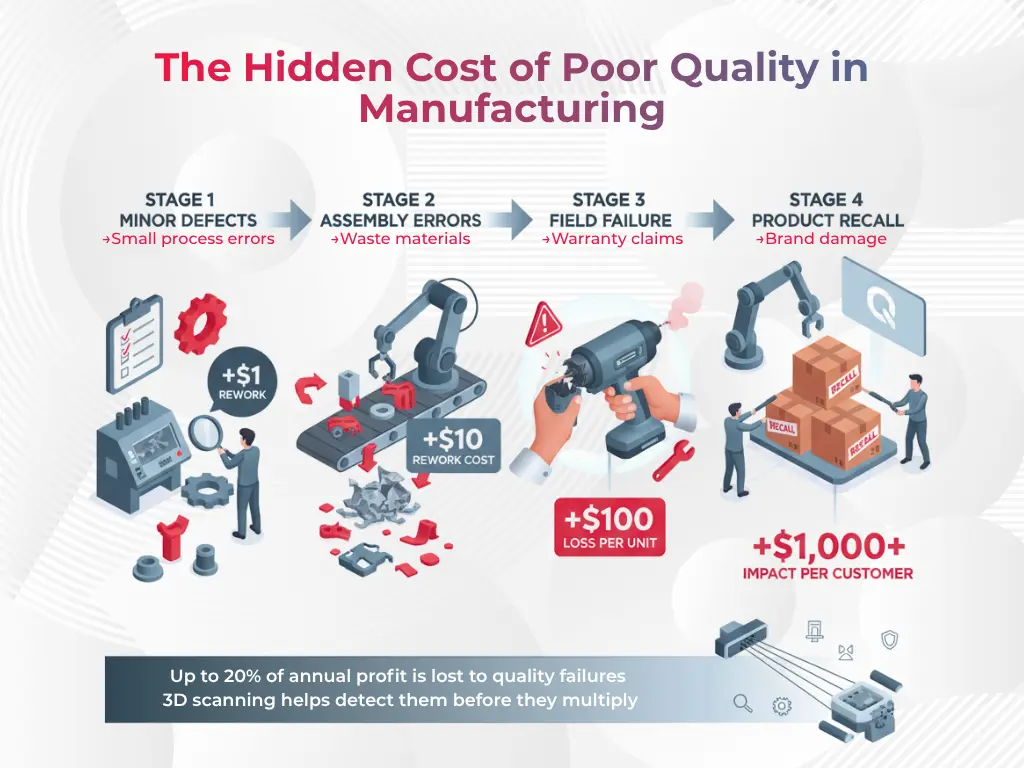
Quality keeps manufacturing professionals up at night. Poor product quality can eat away up to 20% of yearly profits. On top of that, a single bad experience will make 32% of customers abandon a brand completely.
Table of Contents
ToggleQuality control forms the bedrock of manufacturing excellence. Good quality shows that processes work as intended. Any drop in quality points to broken procedures in the production chain. Quality control also affects:
- Material usage and waste minimization
- Environmental regulation compliance
- Supply chain and inventory control
- Production costs and efficiency
- Customer loyalty and brand value
These effects ripple through the entire product lifecycle. The cost of quality problems grows as products move through production stages. Smart manufacturers see quality control not as a cost but as an investment. This investment pays off through less rework, reduced waste, and fewer warranty issues.
Quality control becomes even more vital for companies using advanced technology like 3D laser scanning for measurements. These manufacturing setups need precise consistency. Products must work reliably in different operating conditions. A reliable quality system gives these companies a competitive edge.
How 3D Laser Scanning Improves Dimensional Accuracy
3D laser scanning has transformed the way manufacturers check dimensional accuracy. This touchless measurement technology brings unmatched precision to quality control through several important features:
- Detailed surface capture: Traditional coordinate measuring machines (CMMs) only collect individual points. However, laser scanners capture millions of data points that create complete digital copies of physical objects with precision up to ±0.025mm.
- Complete surface analysis: Rather than taking limited samples, 3D scanning checks entire surfaces. This helps find variations across components that might go unnoticed with other methods.
- Live comparisons: Today’s scanning systems match measured data against CAD models right away. The results show up as color-coded maps that highlight where parts differ from design specs.
- Faster measurements: A single scan captures all geometries at once. This makes inspection up to 80% faster than old methods.
- No human mistakes: The automated nature of laser scanning removes manual measurement variations. This leads to consistent results every time.
- Better record keeping: Each scan creates permanent digital records. These help with tracking, compliance checks, and future reference.
- Better reach: Scanners can measure intricate features and internal surfaces that mechanical probes can’t touch.
The technology also supports statistical process control by analyzing large data samples. This helps manufacturers spot and fix process issues before they exceed tolerance limits.
Integrating Scan Data with Quality Management Systems
Quality excellence in modern manufacturing depends on connecting critical data across systems. 3D laser scanning technology bridges the gap between physical parts and quality management systems to create a complete quality control ecosystem.
- Teams can now combine data from production equipment, shop floor sensors, ERP systems, MES applications, and IoT devices into unified dashboards by integrating scan data with enterprise systems.
- This integrated approach helps identify connections between production conditions and defects that would otherwise stay hidden.
- 3D scanning systems can automatically compare measured parts with reference CAD models. This enables Go/No-Go evaluations, dimensional deviation analysis, and automatic inspection reports. The automation reduces human error and speeds up quality checks.
- Engineers, inspectors, and designers in different locations work better together through cloud-based storage of scan data. The scan data archives also provide complete traceability for audits, warranty reviews, failure analysis, and process improvements.
Quality management integration keeps evolving. These systems can detect and classify defects automatically when combined with artificial intelligence. This shifts quality control from reactive to predictive approaches. Manufacturers who use integrated 3D scanning solutions gain competitive advantages through better product quality, less waste, and improved production efficiency.
Meeting Global Compliance & Industry Standards
Manufacturers must comply with global standards when they implement 3D laser scanning in their quality processes. These regulatory frameworks guide the implementation process for different sectors.
The ISO 10360-8 standard specifically focuses on 3D scanning technologies and creates consistency in scanner performance measurements. This standard covers multiple scanning technologies like triangulation, structured light projection, and confocal systems. It provides two key tests: probing size error to check accuracy in dimensional measurement and probing dispersion to assess measurement noise.
Here are the industry-specific standards that govern 3D scanning implementation:
Industry | Applicable Standards | Typical Accuracy Requirements | Validation Methods |
Aerospace | AS9100, ISO 9001 | – | Typical Accuracy Range |
Automotive | IATF 16949, NAAMS | 0.2 mm for critical dimensions | Precision inspection, component validation |
Medical Devices | FDA regulations, EU 2017/745 | Stringent traceability requirements | Digital record storage for audits |
Construction | USIBD LOA specifications | LOA 30 (±5mm) to LOA 50 (±1mm) | Compare to drawings, control points |
3D scanning lines up perfectly with Industry 4.0 principles and supports critical quality processes. These processes include live decision making, root cause analysis, process optimization, and full traceability. Safety-critical industries and regulatory compliance make these capabilities essential.
Manufacturers should select scanning systems that are certified to relevant standards. This ensures measurement reliability and regulatory acceptance.
Use Cases of Precision Manufacturing with 3D Scanning
Manufacturing companies of all sizes have discovered the value of 3D laser scanning for precision work.
- Aerospace manufacturers need this technology to inspect complex components, especially when checking turbine blade profiles that must be accurate within 0.1mm. One aircraft parts maker cut their inspection time by 63% and found more non-conforming parts after switching to 3D scanning.
- Automotive sector companies use these scanners to speed up prototyping and first article checks. A European car manufacturer found 15% more potential assembly problems with this technology than traditional methods, which helped avoid production delays that could get pricey.
- Medical device makers represent another crucial use case. Companies that produce surgical implants rely on 3D scanning to check vital measurements that affect patient outcomes. The required precision in this field often needs tolerances under 0.05mm, and only non-contact measurement tools can deliver this level of accuracy.
- Consumer electronics companies have found great success with 3D scanning of their tiny components. Smartphone manufacturers can now verify complex housing shapes and internal component spacing with unprecedented accuracy.
Quality teams have taken 3D scanning beyond the production floor to analyze failures and find root causes. Engineers create digital twins of broken parts to study wear patterns and how components deform, which leads to better design choices for future production.
Start building a sustainable future today. Get free 3D Laser Scanning consultation for your project.

Conclusion
3D laser scanning is leading quality control breakthroughs as manufacturing keeps evolving. The technology reshapes inspection processes through complete surface capture, full-field analysis, and immediate comparison capabilities. Manufacturers now achieve precision that traditional measurement methods could never match.
The advantages go nowhere near simple dimensional checks. Companies that use 3D scanning solutions cut their inspection time by up to 80% compared to old techniques. They also spot more potential defects. This quick and accurate process leads to less rework, waste, and warranty claims.
3D laser scanning connects the physical and digital sides of manufacturing effectively. Quality management systems work hand in hand with the technology to create an ecosystem where data moves freely between design, production, and quality checks. Manufacturers can now see patterns in their processes clearly. They spot connections between production conditions and quality results that stayed hidden before.
The technology proves its worth in many industries. It handles aerospace parts with strict 0.1mm tolerances and medical implants that need even more precision. On top of that, it meets global standards while delivering top quality results.
3D laser scanning will without doubt grow stronger with AI and machine learning technologies. This powerful mix will reshape quality control from reactive to predictive approaches. It ended up making 3D scanning essential to achieving manufacturing excellence.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs):
1. What is the role of 3D laser scanning in quality control?
3D laser scanning plays a crucial role in quality control by providing precise, non-contact measurements of manufactured parts. It captures millions of data points to create accurate digital models, enabling manufacturers to identify deviations from design specifications early and ensure product consistency throughout production.
2. How does 3D laser scanning improve manufacturing precision?
3D laser scanning enhances precision by offering full-surface inspection and real-time comparison with CAD models. This technology eliminates human error, accelerates inspection by up to 80%, and ensures every component meets tight dimensional tolerances required in industries like aerospace, automotive, and medical devices.
3. Why should manufacturers integrate 3D scan data with quality management systems?
Integrating 3D scan data with quality management systems allows teams to link inspection results with production conditions. This unified approach improves traceability, identifies root causes of defects, and supports predictive quality control -reducing waste, rework, and warranty claims.
4. Which industries benefit most from 3D laser scanning technology?
Industries that demand high accuracy benefit most -including aerospace, automotive, medical devices, construction, and consumer electronics. From turbine blades to surgical implants, 3D laser scanning ensures tight dimensional control and compliance with global standards like ISO 10360-8 and AS9100.
5. How does 3D laser scanning support Industry 4.0 and smart manufacturing?
3D laser scanning aligns with Industry 4.0 by digitizing quality data and connecting it with IoT, MES, and ERP systems. It creates a continuous feedback loop between design, production, and inspection, enabling real-time decisions, process optimization, and predictive maintenance for zero-defect manufacturing.
6. Why choose TopBIM for 3D laser scanning services?
TopBIM empowers manufacturers with advanced 3D laser scanning solutions that redefine precision and reliability. Our technology-driven approach improves inspection accuracy by up to 80%, supports global compliance, and helps companies transition from reactive to predictive quality control – ensuring manufacturing excellence.
Further Reading
Applications & Risk Management of 3D Laser Scanning in Oil & Gas
3D Laser Scanning for Digital Twin Implementation in Power Plants
Comprehensive Guide on As-Built Surveys
How to Conduct 3D Laser Scanning in Data Centers and Choose the Right Tools?
Comprehensive Guide to 3D Laser Scanning for Power Plants
3D Laser Scanning in Manufacturing: Execution, Tools & Industrial Applications
Our Services
Latest Post
Get A Free Quote
BIM Construction is the Future
Building information modeling (BIM) is the future of building design and construction. Get in touch with our BIM Experts.





