
The USA’s school construction and modernization market is worth more than $100 billion annually. BIM for schools and universities has revolutionized this massive sector, making educational infrastructure smarter and more sustainable. Digital twin BIM software has revolutionized this massive sector and serves as one of the emerging technologies that drive total digitalization of educational infrastructure.
Table of Contents
ToggleBIM adoption comes with challenges like high software costs and training needs. However, these barriers are nowhere near the significant benefits it brings. Projects using BIM have seen a 40% drop in design conflicts and a 15% boost in construction efficiency. Smart campus technology allows managers to make use of information for better decisions. BIM creates a complete digital twin of higher education facilities that handles space booking, sensor monitoring, and asset management.
This piece shows how digital twin development changes traditional campuses into smart learning spaces. You’ll learn about the software used in BIM implementation and its true role as a digital twin. The technology helps leaders make better decisions, measure performance, and boost community participation throughout the campus infrastructure’s lifecycle.
Challenges in Designing Educational Facilities
Budget Challenges in School Construction and How BIM Saves Costs
Money constraints create the most pressing challenge in educational construction.
Designers of educational facilities using BIM face challenges in balancing innovation, sustainability, and cost.
Digital twin BIM software for schools enables architects and planners to visualize, simulate, and optimize layouts that support modern learning.
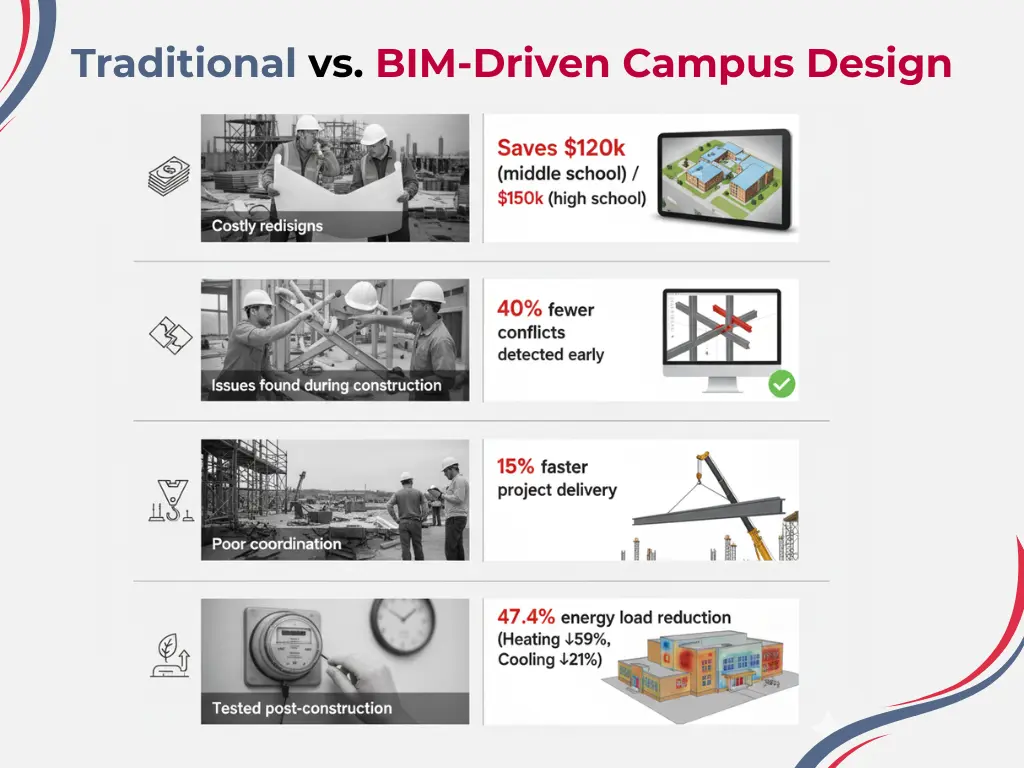
- American schools face an $85 billion yearly shortfall for maintenance and upgrades. This number has grown to $98.6 billion with inflation.
- K-12 institutions just need an extra $429 billion above current budgets through 2033 to improve infrastructure. So, only 5-10% of school budgets support operational costs. BIM technology helps solve these money problems by stopping expensive redesigns.
- Studies show it saves around $120,000 for middle schools and $150,000 for high schools in construction costs.
Managing Multiple Stakeholders in Educational Facility Design with BIM
Educational projects come with a complex web of stakeholders.
- Students, teachers, campus administrators, and maintenance staff make up the core internal group. External partners include taxpayers, parent organizations, booster clubs, nearby property owners, and various authorities.
- Each group brings its own priorities. Administrators care about educational function, maintenance teams focus on longevity, and regulatory bodies ensure compliance.
- BIM visualization helps spot potential conflicts before construction starts, especially when you have competing expectations within educational communities.
Sustainable School and University Design: How BIM Supports Green Goals
Modern educational facilities must follow strict environmental rules.
- Many schools now use tough sustainable design standards. Yale requires LEED Gold certification for new buildings.
- Columbia University wants to reach net zero emissions by 2050. These goals align with rules like Local Law 86/2005.
- BIM helps higher education facilities model energy use and pick sustainable materials. This helps schools balance their environmental goals with limited budgets.
Transform your educational infrastructure with BIM for Universities and Smart Campuses. Claim your free estimate now.
The Role of BIM in Smarter Campus Planning and Educational Space Design
BIM serves as the life-blood of modern campus planning and provides unmatched visualization and analysis capabilities. Digital twin BIM software changes how we design and optimize educational spaces throughout the planning process.
BIM for Site Analysis, Flexible Classrooms, and Multipurpose Learning Spaces
Architectural campus projects start with detailed site analysis to study climatic, geographical, and infrastructural context.
- BIM helps architects assess properties systematically and position buildings based on technical and financial factors. These models work in a geospatial context to compare planned designs against future predictions and create compelling visual representations.
- BIM strengthens architects to create precise 3D classroom models that stakeholders can visualize before construction begins. This precision lets teams explore multiple design options at once. Architects can assess different space configurations, study daylight patterns, and understand how design choices affect costs. Schools designed with hybrid layouts have performed better than all but one of these traditional schools in reading and math tests.
- The move toward multifunctional spaces shows BIM’s most important value. Modern educational environments need spaces that adapt their acoustics, lighting, and materials. BIM aids this adaptability by making modifications easy as educational approaches evolve.
How BIM Improves Safety, Accessibility, and Compliance in Schools
Safety and compliance are crucial for educational facility design. BIM software improves these aspects by a lot throughout a building’s lifecycle.
Fire Safety, ADA Compliance, and Evacuation Simulations with BIM
- Fire incidents create serious threats to educational institutions. Recent years show alarming increases in casualties and property losses. In fact, 2017 alone saw 3,400 deaths and $23 billion in property damage from fires.
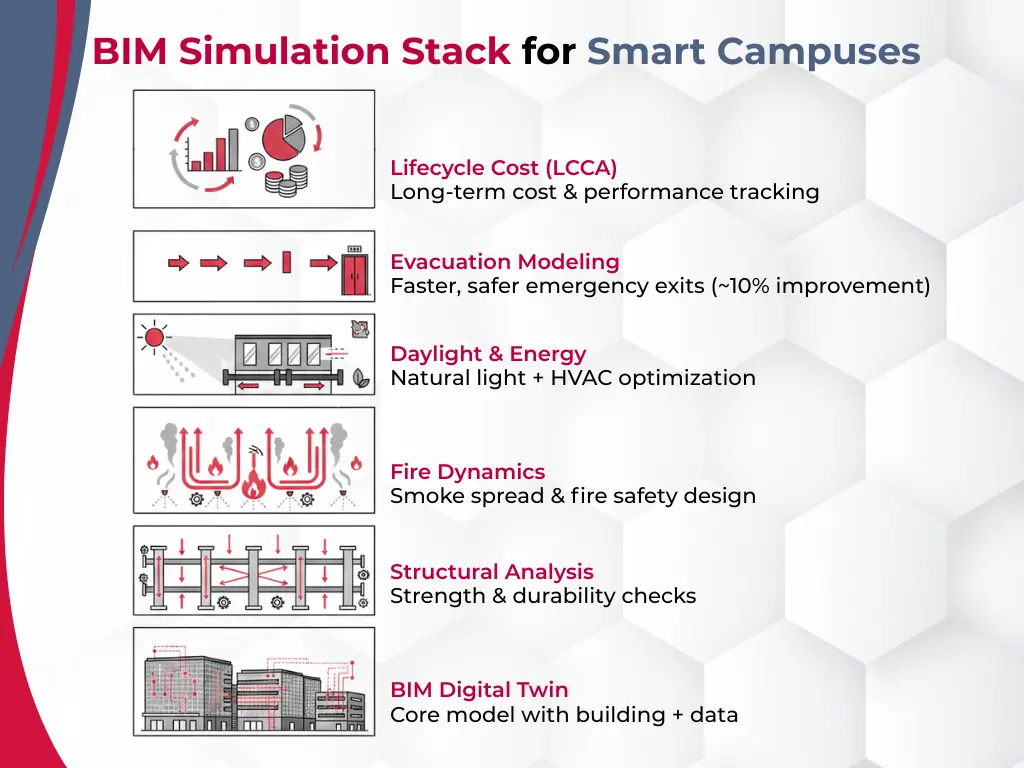
- BIM addresses these concerns through integrated fire dynamics simulation capabilities. Designers can test building performance during fire scenarios. This technology helps visualize hazardous areas, place fire control equipment, and predict smoke spread patterns accurately.
- The aging population has made accessible design more important. BIM changes accessibility planning by embedding ADA requirements directly into modeling processes. Architects can perform automated compliance checks for door widths, ramp slopes, and turning radii. These capabilities help spot potential accessibility issues during design rather than construction. This saves substantial costs and time.
- BIM combined with agent-based modeling creates strong simulations that can improve evacuation time by about 10%. Simulation approaches may vary, but they usually involve generating evacuation routes, analyzing crowd behavior, and spotting potential bottlenecks.
- Educational institutions can develop better emergency protocols that ended up creating safer learning environments for students and staff.
Enhancing Sustainability in Educational Infrastructure with BIM
BIM technology plays a vital role in educational infrastructure sustainability and provides powerful tools to create energy-efficient campuses. Digital twin BIM software serves as the perfect platform to analyze sustainability throughout a project’s lifecycle.
- BIM for Energy Analysis and Lifecycle Cost Estimation in Schools
Energy performance and cost management are two of the most pressing concerns for modern educational facilities. BIM goes beyond design visualization by enabling powerful energy simulations and lifecycle cost assessments. This allows schools and universities to optimize building efficiency, reduce long-term expenses, and achieve green building certifications with measurable results.
Category | BIM Contribution | Impact / Results |
Energy Simulations | Shared energy modeling to test performance under different conditions | Annual energy load ↓ 47.4%; Heating load ↓ 59.1%; Cooling load ↓ 21.5% |
Lifecycle Cost Analysis (LCCA) | Tracks costs from construction → operation → maintenance → end-of-life | HVAC energy ↓ 20%; CO₂ emissions ↓ 30%; Artificial lighting dependency ↓ 25% |
Green Building Certification | Simplifies LEED documentation for energy, water, and indoor air quality | University project: Energy usage ↓ 53.67%; Project cost ↓ 27.48% |
6D BIM Capabilities | Ongoing monitoring & optimization during facility operations | Continuous sustainability management throughout lifecycle |
BIM for Facility Management and Maintenance in School Campuses
Campus facilities management used to store scattered documentation in formats of all types. Digital twin BIM software changes this approach with digital models that support long-term operations.
Using BIM for Long-Term Campus Operations and Renovation Planning
Campus maintenance teams face problems with missing or outdated asset data.
- As-Built BIM models solve this by giving teams a well-laid-out digital system that has equipment details, warranty information, and maintenance schedules.
- Olin College used BIM to simplify their facilities management. They connected building data to their Computerized Maintenance Management System and monitored performance immediately. This helped them respond faster to service requests and control energy costs better.
- Scan-to-BIM technology removes guesswork by capturing existing conditions through laser scanning. This precision helps older educational buildings where accurate documentation affects construction safety.
- The University of Turin’s BIM-GIS integration created a valuable system to track space use, occupancy flows, and indoor environmental quality.
- BIM’s predictive maintenance features are a big step forward from old reactive methods. Maintenance teams can spot potential failures early by using sensor data. This cuts building maintenance costs that make up 65% of yearly facility management expenses.
Case Applications of BIM in Educational Projects
BIM and digital twin technologies are no longer theoretical concepts, they are actively transforming the way educational institutions design, renovate, and manage their facilities. From K-12 schools to large universities, real-world projects across the United States highlight BIM’s adaptability and long-term value.
Elementary School BIM renovation project (USA)
- In a recent project, BIM was applied to modernize the mechanical systems of an elementary school.
Using scan-to-BIM technology, engineers created a LOD 300 mechanical model that enabled accurate clash detection, MEP shop drawings, and 5D quantity take-offs.
- The result was a smoother renovation process, reduced design conflicts, and better coordination among architects, engineers, and contractors.
Endicott College, Massachusetts
- Partnering with Windover Construction, Endicott College implemented a campus-wide Digital Twin for Endicott College that integrates BIM with IoT sensor data.
- This system supports predictive maintenance, streamlines facilities management, and enhances operational decision-making across multiple buildings.
- The project demonstrates how digital twins can unlock smarter campus operations.
University of Texas at Austin (UTwin Project)
- UT Austin has developed UTwin, a pioneering digital twin platform that combines building data with geospatial information. This initiative enables advanced energy modeling, sustainability planning, and resource optimization for one of the nation’s largest university campuses.
The University of Texas’s UTwin project is a leading example of smart campus BIM implementation in higher education.
Together, these case studies illustrate how BIM adapts to different scales and contexts, whether upgrading a single elementary school, improving campus-wide operations, or modeling energy use across a major university.
Conclusion:
The application of BIM in educational infrastructure is moving beyond design efficiency into the realm of integrated digital asset management. The next wave of smart campuses will rely on digital twins not only to track energy and lifecycle costs but also to integrate IoT sensor networks, predictive analytics, and real-time space utilization data. This convergence will transform BIM from a project delivery tool into a continuous decision-support system for administrators and facility managers.
As machine learning models are layered onto digital twin environments, campuses will gain the ability to forecast maintenance issues, optimize resource allocation, and simulate emergency or occupancy scenarios with unprecedented accuracy. In practice, this means educational institutions adopting BIM today are laying the groundwork for autonomous, self-optimizing campuses, a shift that aligns physical infrastructure with both pedagogical evolution and long-term sustainability goals.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs):
How is BIM transforming planning and delivery of large educational campuses?
BIM enables integrated master planning, multi-building coordination, and phased development by providing a single digital model that aligns architects, engineers, contractors, and campus administrators.What challenges do educational institutions face without BIM adoption?
Without BIM, campuses often experience design clashes, inefficient space utilization, higher lifecycle costs, poor coordination during expansions, and limited visibility for long-term facility management.How does BIM support future-ready campuses and Smart Education initiatives?
BIM lays the foundation for smart campuses by supporting digital twins, IoT integration, sustainability tracking, and data-driven decision-making across academic, residential, and operational facilities.Why is BIM important for educational facilities and campus planning?
BIM helps educational institutions design flexible learning spaces, optimize land use, improve collaboration, and ensure cost control while supporting long-term campus growth and operational efficiency.Can BIM support maintenance and operations after campus construction is complete?
Yes. BIM models store detailed asset and system data that can be used for facility management, preventive maintenance planning, space management, and future renovations or expansions.
Our Services
Latest Post
Get A Free Quote
BIM Construction is the Future
Building information modeling (BIM) is the future of building design and construction. Get in touch with our BIM Experts.





