
Getting accurate data from your laser scanning project isn’t just about having the right equipment, it’s about choosing the right partner who knows how to turn raw point clouds into actionable results. If you’re a facility manager, architect, or construction professional evaluating laser scan data processing and scanning providers, understanding what happens behind the scenes can save you from costly mistakes and project delays.
Table of Contents
ToggleThis guide breaks down the complex world of laser scan data processing and provider selection into practical insights you can use today. We’ll walk through the essential data processing steps that transform millions of data points into usable CAD drawings and BIM models, then show you exactly what to look for when choosing between laser scanning service providers and technologies.
What Happens to Your Data After a Laser Scanning Service?
When your laser scan data processing begins, the captured point cloud data undergoes systematic organization and verification.
- Professional scanning solutions ensure all captured data points are properly stored with sufficient data storage space, while the scanning accuracy defined during initial project planning (whether 1mm or 5mm precision) is validated through quality checks and calibration settings review.
- The processed point cloud data becomes the foundation for advanced applications, with well-placed targets and control points serving as reference markers for precise alignment during post-processing.
- Strategic positioning of reflective spheres and checkerboard patterns ensures optimal visibility from all scan positions, enabling seamless data integration and minimizing occlusions for comprehensive 3D laser scanning technology results.
Start building a sustainable future today. Get free 3D Laser Scanning consultation for your project.
Cost vs. Value: What Really Drives ROI
Balancing cost and value are about more than price, here’s what really drives ROI in laser scanning projects.
Cost Drivers
- Equipment Type – Terrestrial, Drone, Mobile Scanners
- Scope & Scale – Single floor vs. campus-wide facility
- Level of Detail (LOD) – LOD 200 vs. LOD 400 BIM models
- Deliverables – Point cloud only vs. full Scan-to-BIM
Value Beyond the Price Tag
- Reduced rework & RFIs with accurate as-builts
- Faster approvals with precise documentation
- Long-term asset value through digital twins for FM teams
- Improved safety with fewer site revisits
How Do Professional Providers Handle Laser Scan Data?
Professional laser scanning service providers follow systematic workflows to transform raw scan data into usable deliverables.
- The process begins with secure scanner mounting on stable tripods and strategic positioning according to predetermined scanning plans.
- Providers capture multiple overlapping scans from various positions, ensuring comprehensive coverage while maintaining registration accuracy through carefully placed reference targets.
- Now that multiple scans are collected, laser scan data processing specialists focus on alignment and quality verification.
- They align individual scans using reference targets and meticulously verify registration accuracy to identify potential misalignments or errors in the point cloud data. This cleaning phase is critical for professional scanning solutions, as providers must correct any discrepancies before converting the processed data into CAD BIM conversion services formats for client deliverables.
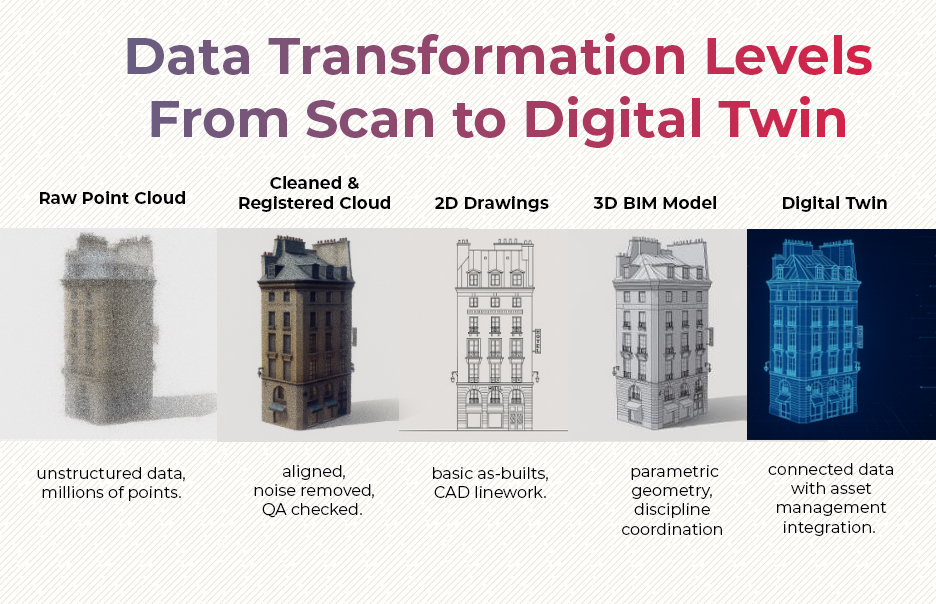
Which Tools and Technologies Do Experts Use for Processing?
Technology Type | Best Use Case | Accuracy Level |
Terrestrial Laser Scanners | Large-scale facilities, interiors | Sub-millimeter precision |
Mobile Scanning Systems | Linear infrastructure, fast capture | Moderate precision |
Drone LiDAR Systems | Site grading, topography, outdoors | Varies (depends on drone + sensor) |
Software Platforms:
- Registration & Cleanup: Leica Cyclone, FARO Scene, Trimble RealWorks
- Modeling: Autodesk Revit, Navisworks, Bentley
- Deliverables: Multiple file formats (RVT, DWG, IFC, etc.)
Laser Scanning Vs LiDAR Solutions – What’s the Difference?
Aspect | Terrestrial Laser Scanning | Drone LiDAR |
Accuracy | Very high (sub-mm to few mm) | Moderate to high |
Best for | Interiors, MEP, detailed as-builts | Large outdoor sites, terrain |
Coverage | Limited per scan, requires multiple positions | Wide area coverage in less time |
Environment | Controlled, smaller zones | Rugged, open, long-range areas |
How to Decide the Right Solution or Provider for Your Project?
Red Flags to Avoid:
- Unrealistic accuracy claims.
- Promises of “fastest timelines” without methodology.
- Pricing that’s too good to be true.
- Limited portfolio or vague service descriptions.
- Outdated equipment and lack of certifications.
What to Look For in a Provider:
- Proven industry experience and relevant case studies.
- Updated scanning technology suited to your project.
- Rigorous QA/QC protocols.
- Deliverables in compatible file formats.
- Insurance and certifications for liability coverage.
- Clear communication and ongoing support.
The success of a scanning project ultimately relies on a clear understanding of the entire data journey, from raw capture to final deliverables, combined with the selection of providers who bring proven expertise, rigorous quality assurance, and advanced technology investments to the table. Rather than focusing solely on cost, it’s essential to evaluate providers based on their technical quality, accuracy verification processes, and ability to deliver compatible outputs. By choosing the right partner, you ensure that raw point clouds are transformed into accurate CAD drawings, BIM models, or digital twins, keeping your projects precise, efficient, and on budget.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs):
Q1. What happens to the data after a laser scanning project is completed?
After scanning, the raw point cloud data goes through systematic organization, alignment, and quality verification. Technicians ensure precision by using reference targets, removing errors, and preparing the data for conversion into CAD drawings or BIM models.
Q2. How do professional providers ensure accuracy in laser scan data processing?
Providers follow strict QA/QC protocols, including cross-checking control points, validating dimensions against known references, and running Scan-to-CAD/BIM accuracy checks. This ensures the final deliverables are reliable and precise.
Q3. Which technologies are commonly used for laser scanning and data processing?
Experts use terrestrial laser scanners for interiors and detailed as-builts, mobile systems for fast linear infrastructure scanning, and drone LiDAR for large outdoor sites. Software like Leica Cyclone, FARO Scene, Trimble RealWorks, and Autodesk Revit are widely used for registration, modeling, and deliverables.
Q4. What is the difference between terrestrial laser scanning and drone LiDAR?
Terrestrial scanning provides very high accuracy (sub-millimeter to a few millimeters) and is best for interiors and MEP documentation, while drone LiDAR covers wide outdoor areas quickly with moderate-to-high accuracy, making it ideal for topography and site grading.
Q5. What factors drive the cost of a laser scanning project?
Costs depend on the type of equipment used (terrestrial, drone, or mobile), the scope and scale of the project, the required level of detail (LOD), and the deliverables (point cloud only vs. full Scan-to-BIM).
Q6. What should I look for when selecting a laser scanning provider?
Choose providers with proven experience, updated technology, strong quality control processes, compatible deliverables, proper certifications, and clear communication. Avoid providers with unrealistic promises, outdated equipment, or unclear portfolios.
Q7. Why is it important to focus on value and not just cost when selecting a scanning solution?
While cost is a factor, value comes from reduced rework, faster project approvals, safer operations, and long-term asset benefits like digital twins. A slightly higher investment in quality scanning can save significant time and costs later.
Further Reading:
What is Laser Scanning in Surveying and How Can These Solutions Benefit Your Business?
BIM for Sustainability and Energy Efficiency Modeling
Building Information Modeling for Infrastructure : Comprehensive Guide
Competitive Advantages Of BIM Automation In The AEC Industry
BIM for Heritage Preservation – Future of Protecting Our Past
Future-Proofing AEC Projects: The Role of BIM in Meeting Both ADA and OSHA Standards
Our Services
Latest Post
Get A Free Quote
BIM Construction is the Future
Building information modeling (BIM) is the future of building design and construction. Get in touch with our BIM Experts.





