Data center management relies heavily on 3D laser scanning as an essential tool. This technology gives a unique experience in documenting existing conditions, especially when you have complex environments full of critical infrastructure. The best 3d laser scanner for buildings captures millions of data points that create a complete digital twin of the physical space, unlike traditional measuring techniques.
Table of Contents
TogglePurpose- accuracy, efficiency, cost savings
- LiDAR scanning technology’s value in data centers comes from its amazing accuracy. Modern scanners capture measurements down to millimeter precision.
- This precision is vital when planning rack layouts, cooling systems, and cable pathways. Teams can work with exact spatial data instead of approximations, which speeds up renovation projects and expansions.
- The cost savings make a significant impact. Data center operators can avoid expensive rework from spatial conflicts or design errors by creating detailed digital models before physical work starts.
- Finding just one clash during planning can save tens of thousands of dollars in construction remediation costs. This technology pays for itself by reducing downtime risks in mission-critical facility documentation.
Site assessment:
- A full picture must happen before any scanning project begins. Specialists need to identify key infrastructure elements for documentation and determine the best scanning positions for coverage.
- They review the environment’s complexity to pick the right building laser scanner technology, whether terrestrial, handheld, or mobile systems.
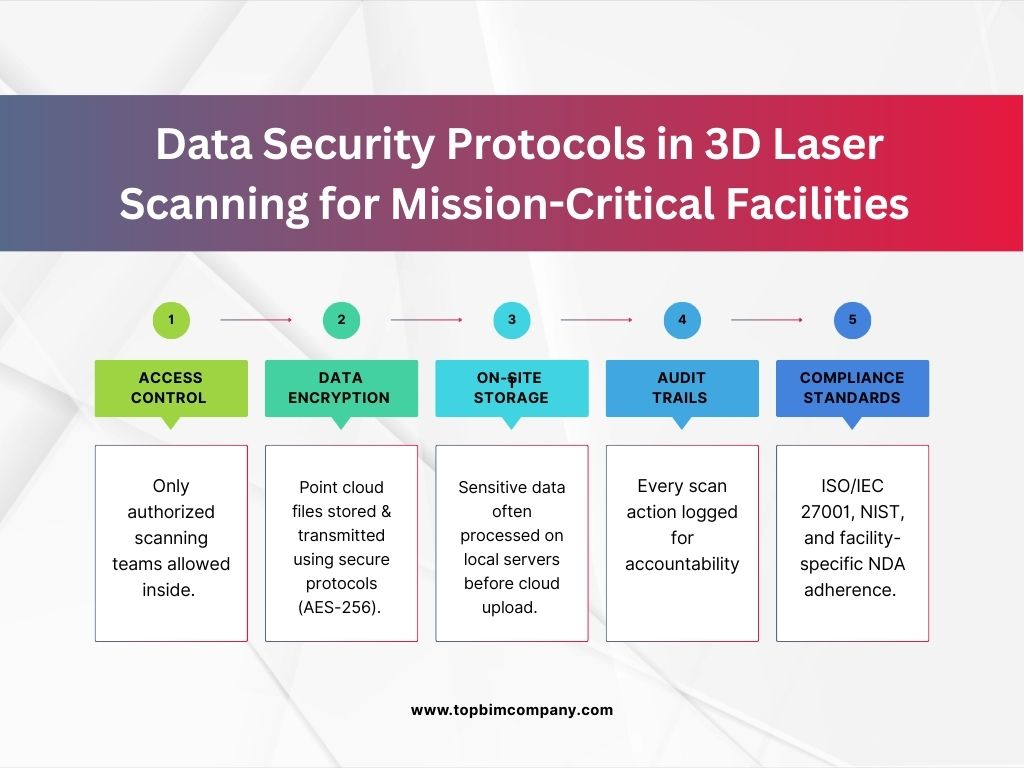
- Data centers house sensitive information, so security is paramount. Scanning teams follow strict protocols for data handling, storage, and transmission of the captured point cloud data.
Pre-scan checklist
This checklist helps ensure successful data center scanning:
- Getting access permissions and security clearances
- Spotting critical equipment that must stay in place
- Finding the best scanning times to keep disruption low
- Checking power availability for scanning equipment
- Setting up data handling protocols that match facility security needs
- Getting temporary targets or reference points ready for scan alignment
- Listing areas that need extra attention or higher resolution scans
Good preparation using this checklist lets teams conduct 3D laser scanning efficiently while protecting data center operations and security. The resulting point cloud data processing creates solid foundations for future infrastructure planning and management.

Start building a sustainable future today. Get free 3D Laser Scanning consultation for your project.
What Preparations Are Needed Before a Data Center Scan?
Good planning and preparation are the foundations of effective 3D laser scanning in data centers. A complete site assessment helps identify potential challenges and optimize the scanning process. The assessment has to evaluate access points, environmental conditions, and safety considerations that might affect the quality of point cloud data processing.
Make sure to talk with all stakeholders about how to use the scan data before arriving on-site. This vital step will give everyone from technical teams to architects a clear picture of how deliverables will meet their needs. On top of that, a quick sketch of the scanning site helps us figure out the best scanner positions and spot physical limitations that could affect the project.
The team must complete several essential checks before powering up any 3D laser scanning equipment:
- Verify scanner functionality and battery levels
- Ensure tripod stability and proper attachment
- Check for damage to scanner casing or mirror
- Confirm adequate data storage capacity
- Plan power needs for longer scanning sessions
Safety comes first throughout the preparation process. Only trained personnel who understand all safety documentation should operate the best 3D laser scanner for buildings. Data center teams must create detailed continuity plans that could include temporary cooling units to maintain performance during scanning.
A clear project scope prevents return visits that can get pricey. Teams should specify which areas need scanning interior/exterior spaces, occupied/unoccupied areas, number of floors, and outline the required deliverables and timeline.
How to Perform the Laser Scanning Process Step-by-Step?
The execution phase of 3D laser scanning turns careful preparation into useful data. A systematic approach will give you accurate and efficient results throughout the scanning process.
Field workflow with service checklist
A successful data center scan needs a step-by-step sequence:
- Equipment setup – Place your building laser scanner on stable ground and make sure it’s level before turning it on. The scanner’s height should capture both floor and ceiling elements effectively.
- Target placement – Place reference targets across the space, especially at intersections and corners. This makes point cloud alignment more accurate later.
- Scanner configuration – Choose the right resolution and quality settings based on your detail needs. Higher settings give more detail but take substantially longer to scan.
- Systematic scanning sequence – Begin from one corner and work your way through the facility. Each scan position should overlap with previous ones by at least 30% to ensure proper registration.
- Quality verification – Take a quick look at the captured data after each scan before moving forward. This helps avoid return visits that can get pricey.
Keep a detailed field log of scan positions, resolution settings, and any challenges you face on site. This documentation is a great way to get help during point cloud processing and Revit model integration.
Note that scanner operation in tight data center spaces often needs adjustments to standard procedures. This helps you work around active equipment while keeping precision intact.
What Tools and Technologies Are Best for Data Center Scanning?
Data center documentation’s success depends heavily on choosing the right scanner technology. Each scanning tool’s precision, mobility, and data capture capabilities significantly affect project results.
- Terrestrial Laser Scans
- Leica ScanStation P50’s range capabilities are a big deal as it means that they exceed 1 kilometer with millimeter-level accuracy, making it perfect for large data center spaces.
- These tripod-mounted devices create ultra-dense point clouds by capturing about 1 million points per second, which seamlessly integrate into Revit models.
- Handheld Laser Scanner:
- Handheld scanners shine in tight data center spaces. To name just one example, see the Leica BLK2GO that lets you capture 3D environments by walking through the facility.
- This quickest way to scan reduces on-site time and works great for documenting complex cable pathways and rack layouts.
- Mobile Scanners:
- FARO Orbis and similar mobile mapping systems blend terrestrial scanning’s benefits with SLAM technology.
- These systems capture data ten times faster than conventional methods. Their 120-meter maximum range delivers the speed and precision needed for detailed data center infrastructure mapping.
Software comparison table
Software Feature | Leica Cyclone | FARO Sphere XG | Trimble RealWorks |
Real-time visualization | Yes | Yes | Limited |
Cloud connectivity | Yes | Yes | Yes |
Automated registration | Yes | Yes | Yes |
BIM integration | Advanced | Good | Advanced |
Point cloud editing | Comprehensive | Good | Comprehensive |
How is Data Captured, Processed, and Modeled for Clients?
A sophisticated workflow converts raw scan data into practical client deliverables. The process transforms spatial information through multiple stages and adds value at each step.
Point clouds, BIM models, and deliverables
The building laser scanner data first goes through registration to create a unified point cloud. This combined dataset creates a digital copy of the facility with millimeter precision. Registration software spots common points between scans through target-based or cloud-to-cloud alignment methods.
Point cloud processing cleans the data through noise reduction, decimation, and segmentation. These steps remove incorrect points while keeping the data center infrastructure’s critical details intact. The cleaned point cloud becomes the base for all future deliverables.
Data modeling creates practical formats for complex facilities. Point cloud data processing generates:
- 3D BIM models with precise equipment positioning
- 2D CAD drawings for traditional documentation
- 360° panoramic views for virtual facility tours
- Clash detection reports highlighting spatial conflicts
Quality control checkpoints verify accuracy and completeness throughout this workflow. The Revit model integration stage needs special focus because it turns abstract point data into intelligent objects that represent real-life components. The final deliverables give data center operators detailed documentation that helps with capacity planning and disaster recovery scenarios.
What Outputs Can You Expect From a Professional Scanning Service?
3D laser scanning services produce a suite of valuable deliverables that change raw spatial data into useful business insights. Clients receive finalized assets to address specific operational needs after scanning and processing phases.
Documentation, 3D models, compliance-ready reports
Detailed documentation contains as-built drawings that accurately reflect the data center’s current conditions. These CAD drawings show floor plans, equipment layouts, and essential measurements in formats that work with industry-standard design software.
Point cloud data processing creates highly detailed 3D models that go beyond simple documentation. These digital twins let users visualize complex spaces interactively and enable virtual walkthroughs from anywhere. Stakeholders can access intelligent BIM objects through Revit model integration. These objects represent actual infrastructure components and contain embedded metadata.
The most practical deliverables consist of:
- Clash detection reports that highlight spatial conflicts between proposed changes and existing infrastructure
- Virtual reality environments to support remote collaboration and training
- Panoramic imagery for easy visual reference
Compliance-ready reports serve as significant outputs for regulated industries. These specialized deliverables show spatial clearances, emergency access paths, and equipment positioning to prove adherence to safety standards and building codes. The best building laser scanner services ended up providing deliverables that support immediate operational needs and long-term facility management goals.
Conclusion
3D laser scanning in data centers does more than accelerate documentation, it reshapes how operators think about infrastructure itself. By converting physical complexity into digital clarity, scanning enables decision-makers to model “what if” scenarios, anticipate risks before they happen, and future-proof facilities for scalability.
The true inference is this: data centers that embed scanning into their lifecycle aren’t just documenting space , they are building resilience. Every clash avoided, every compliance check automated, and every rack layout optimized becomes a competitive differentiator in an industry where downtime costs millions and trust is non-negotiable.
In that sense, scanning is not a back-office process but a strategic asset. It provides the intelligence layer that makes capacity planning more precise, sustainability goals more achievable, and digital transformation initiatives more grounded in reality. Operators who treat laser scanning as integral to facility strategy will lead not only in operational efficiency but also in market agility.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs):
1. Why is 3D laser scanning important for data centers?
3D laser scanning provides millimeter-level accuracy for documenting existing infrastructure. This precision reduces rework, prevents costly clashes, improves space utilization, and ensures compliance in mission-critical facilities.
2. How does 3D laser scanning compare to traditional documentation methods?
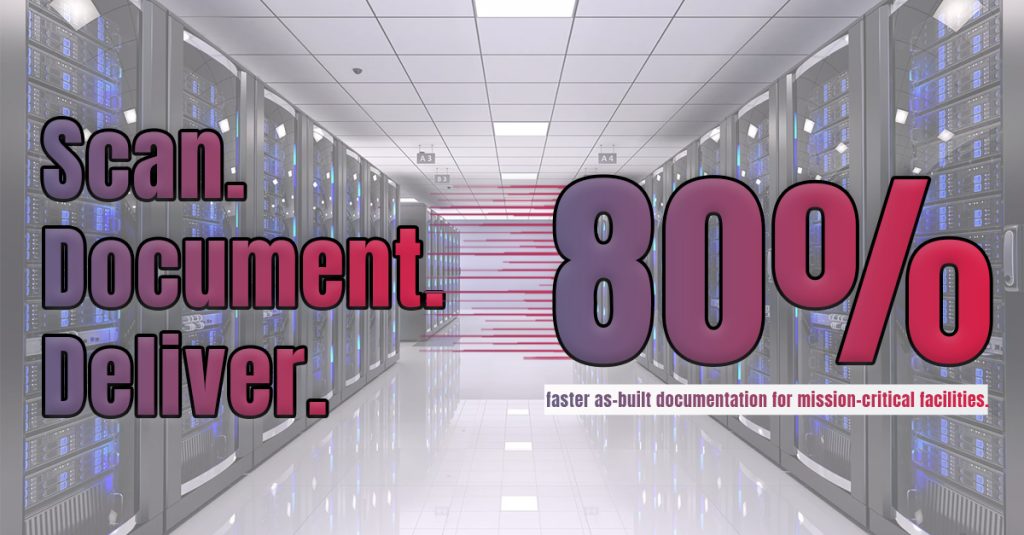
Unlike manual measurement, which often leads to errors and inefficiencies, laser scanning captures millions of data points to create a digital twin. This results in faster documentation (up to 80% quicker), improved accuracy, and reduced downtime risks.
3. What preparations are required before starting a data center scan?
Preparations include obtaining access permissions, identifying critical equipment, scheduling scans to minimize disruptions, checking scanner readiness, and setting strict data security protocols. A clear project scope helps avoid costly return visits.
4. Which laser scanning tools are best for data centers?
Terrestrial scanners (e.g., Leica ScanStation P50) for large-scale, high-accuracy scans.
Handheld scanners (e.g., Leica BLK2GO) for tight or complex spaces.
Mobile scanners (e.g., FARO Orbis) for fast data capture using SLAM technology.
5. How is the scan data processed after capture?
Raw scans are registered into a unified point cloud, cleaned for noise, and segmented. From this, deliverables such as BIM models, CAD drawings, clash detection reports, and VR walkthroughs are generated for practical use.
6. What deliverables can clients expect from a professional scanning service?
Clients receive:
As-built CAD drawings
3D BIM models/digital twins
Clash detection reports
Panoramic imagery
Compliance-ready documentation for audits and approvals
7. How does laser scanning help reduce costs in data centers?
By detecting clashes before construction, operators can save $10k–$50k per remediation. Scanning also reduces downtime risks (which can cost $100k–$500k per hour for hyperscale facilities) and improves efficiency in rack/cooling layouts.
8. Is 3D laser scanning secure for sensitive facilities?
Yes. Professional scanning follows strict data security protocols including access control, AES-256 encryption, on-site storage, audit trails, and compliance with ISO/IEC 27001, NIST, and NDA requirements.
9. Can laser scanning be used for both new builds and renovations?
Absolutely. Scanning supports new data center construction, expansions, and renovations by providing highly accurate as-built documentation that eliminates surprises during execution.
10. What industries benefit most from data center laser scanning?
While designed for mission-critical facilities like data centers, industries such as healthcare, manufacturing, energy, and telecom also leverage 3D scanning for compliance, efficiency, and cost reduction.
Further Reading
What is Laser Scanning in Surveying and How Can These Solutions Benefit Your Business?
How As-Built Drawings Ensure Compliance with Building Codes
BIM for Sustainability and Energy Efficiency Modeling
Competitive Advantages Of BIM Automation In The AEC Industry
BIM for Heritage Preservation – Future of Protecting Our Past
Future-Proofing AEC Projects: The Role of BIM in Meeting Both ADA and OSHA Standards
Our Services
Latest Post
Get A Free Quote
BIM Construction is the Future
Building information modeling (BIM) is the future of building design and construction. Get in touch with our BIM Experts.





