
Poor maintenance strategies can reduce production capacity by 5 to 20 percent. Power plants have recognized this significant loss and are now turning to 3D laser scanning technology to improve their maintenance planning and asset management.
Table of Contents
ToggleThe technology leverages high-speed LiDAR to capture millions of measurement points, creating a point cloud that represents the exact shape, size, and spatial relationships of physical environments. Companies can build visual, cloud-based digital twins of their operations by digitizing facilities through 3D laser scans. A leading US-based OEM has successfully implemented this approach across 40 million square feet of its global manufacturing space.
The results speak for themselves. McKinsey projects that digital maintenance in the industry can boost asset availability by 5 to 15 percent and cut maintenance costs by 18 to 25 percent. Manufacturers who use these 3D scanning plant solutions have reported up to 50% less rework through enhanced visualization and validation. This piece explores how 3D laser scanners help power plants spot potential problems early and prevent expensive failures before they happen.
Importance of Maintenance Planning in Power Plants
“Laser scanning clearly represents the future of our business and every business that depends on being able to quickly and accurately determine the geometry of a physical part.” — Turbine OEM (as cited by NVision, Inc.),
Maintenance planning is the life-blood of successful power plant operations. The financial toll of poor maintenance hits hard in an industry where reliability matters most. Industrial facilities lose an average of USD 124,669 per hour from unplanned downtime. Almost 70% of sites face these disruptions at least once a month. These numbers show why maintenance must stay a top priority.
Strategic maintenance directly affects how smoothly a power plant runs. Equipment that’s well-maintained runs more efficiently and uses less energy while keeping optimal output. This leads to lower operational costs and better environmental performance with fewer emissions.
- Good maintenance does more than just help daily operations. It makes equipment last longer too. Studies reveal that well-run preventive maintenance programs can make equipment last 20-40% longer and reduce downtime by 30-50%.
- Advanced inspection programs can push maintenance intervals from five to seven years. This helps plants manage their resources and plan better.
- Safety remains crucial in power plant settings. Poor maintenance puts worker safety and environmental protection at serious risk. Regular checks and upkeep help spot potential dangers before they turn into hazardous situations or break regulations.
- Numbers make a strong case for structured maintenance. Proactive maintenance saves two to five times more money than reactive approaches. This happens because planned fixes prevent total breakdowns that need emergency repairs at premium costs.
- Modern facilities now mix preventive and predictive approaches as maintenance strategies evolve. Preventive maintenance follows set schedules whatever the equipment’s condition. Predictive maintenance makes use of data analytics and sensors to track asset health as it happens. Both methods help create a more reliable power generation process when done right.
- Plant managers who want to boost operational excellence should set clear maintenance protocols. They can rank issues by severity (critical, important, monitoring) to create a framework that works. This approach makes sure critical systems get quick attention while making the whole maintenance process more efficient.
How 3D Scanning Supports Predictive Maintenance
3D laser scanning has changed power plant maintenance from reactive to predictive by creating exact digital copies of physical assets. These detailed scans can spot early signs of equipment wear that human eyes cannot detect.
Survey-grade terrestrial scanners capture detailed point clouds of the equipment. Plant managers compare these scans with baseline models to spot any changes that might signal problems. This analysis shows exactly how much an asset has moved from its original specs.
A real-life example shows how one refinery used 3D laser scanning to spot dangerous wear in a compressor unit. This timely discovery prevented a complete breakdown. Ball mill operators now use 3D scans to predict liner life more accurately than traditional ultrasonic testing.
This technology delivers impressive results-manufacturers have cut rework by up to 50% through better visualization. The approach helps maintenance teams to:
- Spot changes in geometry, misaligned parts, and worn surfaces
- Plan repairs based on actual equipment condition instead of fixed schedules
- Combine scan data smoothly with vibration sensors and temperature probes for detailed health monitoring
3D scanning creates data-rich digital twins that let teams make maintenance decisions based on actual physical conditions rather than guesswork or old drawings.
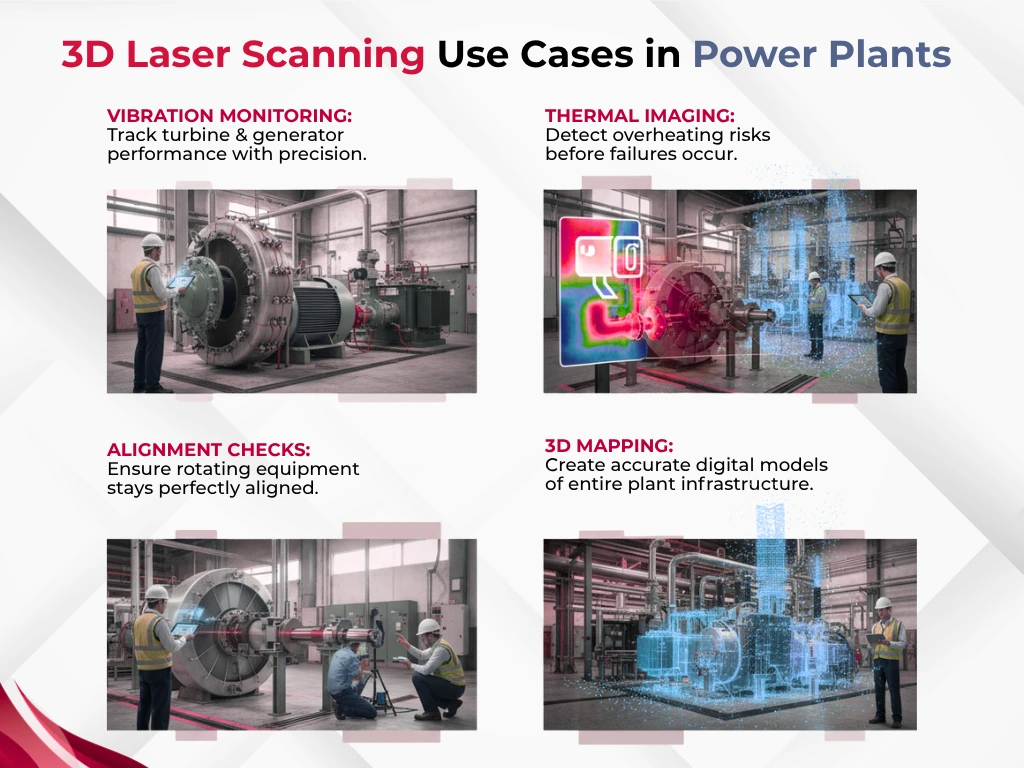
Detecting Equipment Wear, Corrosion, and Structural Issues
“The scans revealed several potential clashes early in the design process, allowing the project team to avoid hundreds of thousands of dollars in rework costs while staying on schedule.” — TopBIM Company Editorial Team, Industry experts in BIM and 3D scanning for power plants
Power plant operations benefit from early detection of equipment wear and corrosion that reduces unexpected failure risks. 3D laser scanning technology stands out by capturing equipment surfaces and structures with millimeter-accurate measurements.
The technology shows remarkable precision. It takes measurements accurate to 1/4″ from distances of 100 meters or more. Advanced systems can capture up to 2,600,000 points per second. This detailed scanning enables detection of:
- Structural cracks and deformations before they compromise integrity
- Surface corrosion patterns that traditional methods might miss
- Misalignments in critical components
- Thermal anomalies when combined with thermal sensors
Corrosion remains a common source of damage in aging power infrastructure. This damage occurs more frequently in areas where malfunctioning expansion joints allow water to reach bearing areas. Steel member’s corrosion tends to be topologically non-uniform and random, which makes traditional inspection methods less effective.
Manual techniques depend heavily on technician skill and environmental conditions. 3D scanning delivers user-independent, repeatable results instead. This independence from human error is significant because traditional inspections require technicians to work in difficult positions. They often lie on the ground or hang from ropes, which makes finding the deepest corrosion points challenging.
Start building a sustainable future today. Get free 3D Laser Scanning consultation for your project.
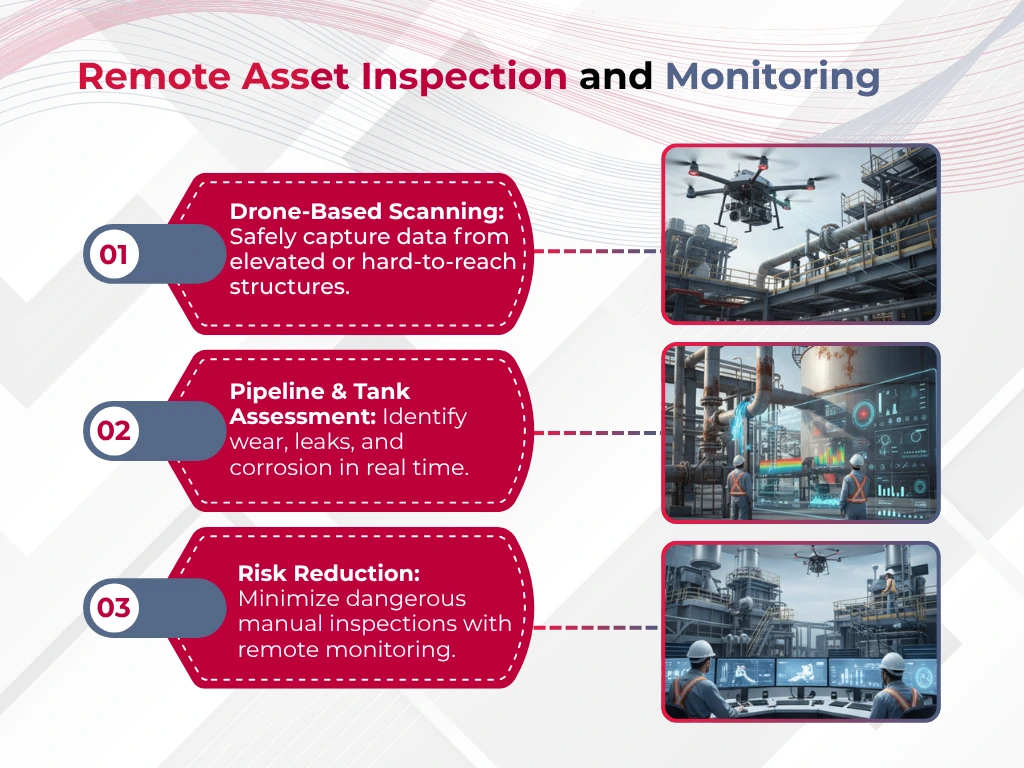
Integrating Scan Data with Asset Management Systems
3D laser scanning shows its real worth in power plants when scan data combines smoothly with Enterprise Asset Management (EAM) systems. This combination creates a digital feedback loop that keeps virtual and physical assets in sync with up-to-the-minute updates.
Today’s Scan-to-EAM workflows merge reality capture data with asset identification and feed directly into EAM solution databases. The process captures three key data types: 3D point clouds, area images, and GeoTags. These components create a complete digital twin that serves as the foundation for asset management decisions.
The integration of these systems brings significant operational advantages:
- Simplified maintenance planning with virtual access to asset locations
- Better collaboration between departments through cloud-based platforms
- Automated detection of deviations that need maintenance
- Improved visibility of mission-critical assets for evidence-based decisions
These systems can adapt to work with other enterprise solutions. BIM integration produces detailed interactive models for facility management. GIS integration allows spatial analysis for planning. Power plants using Computer Aided Facilities Management (CAFM) software can access web-based visualization tools that provide immersive Google Street View-style panoramas of indoor spaces.
This integration changes how power plants maintain critical equipment. It connects physical realities with digital intelligence and helps maintenance teams spot problems virtually before entering potentially dangerous environments.
Condition-Based Maintenance Using 3D Scans
Aspect | Details / Examples | Value / Benefits |
Definition | CBM replaces scheduled maintenance with systems that trigger alarms before failure. | Moves plants from reactive to predictive strategies. |
Case Example | University of Toronto mapped steam pipes using 3D scanning. | Protected historic buildings & reduced excavation risks. |
Technology Used | Portable scanners (e.g., RTC360) to capture complete 3D data in tight spaces. | Builds accurate digital twins of assets. |
Advantages | – Immediate prognostics | Extends asset life, cuts downtime, reduces risks. |
Integration Example | Mumberg Engineering combined 3D scanning with ultrasonic testing for pipe inspections. | Captures 1.5M+ measurements/sec → enables quick, data-driven maintenance decisions. |
Conclusion
The integration of 3D laser scanning into power plant operations marks a decisive shift in how facilities manage their assets. What was once a reactive process, fixing equipment only after failures, has evolved into a predictive and condition-based framework where issues are identified before they escalate. The ability to generate millimeter-accurate digital twins allows maintenance teams to visualize plant conditions in real time, detect early-stage wear or corrosion, and plan interventions with far greater precision.
This shift not only reduces downtime and extends the lifespan of critical machinery but also strengthens operational safety by minimizing the need for hazardous manual inspections. Moreover, when connected with Enterprise Asset Management (EAM) and BIM systems, scan data becomes a central intelligence layer that keeps digital models in sync with physical assets, enabling evidence-based decision-making across departments.
In essence, 3D laser scanning transforms maintenance from a necessary expense into a strategic lever for efficiency, sustainability, and reliability. For power plants facing increasing pressure to deliver uninterrupted energy at lower costs, the adoption of this technology is no longer optional, it is the foundation for long-term resilience and competitiveness in the energy sector.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs):
1. What is 3D laser scanning for power plant maintenance?
3D laser scanning for power plant maintenance uses LiDAR-based sensors to capture millions of precise data points, creating detailed 3D models or digital twins of plant equipment for accurate inspection and analysis.
2. How does 3D laser scanning support predictive maintenance?
3D laser scanning helps detect early signs of equipment wear, corrosion, or misalignment. These insights allow power plants to schedule predictive maintenance before breakdowns occur, reducing unplanned downtime and repair costs.
3. Why is predictive asset management important in power plants?
Predictive asset management minimizes unexpected failures, improves energy efficiency, extends equipment lifespan, and enhances safety — ensuring continuous, cost-effective power generation.
4. How does TopBIM implement 3D laser scanning in power plant projects?
TopBIM combines high-speed LiDAR scanning with BIM and Enterprise Asset Management (EAM) systems to create accurate digital twins, enabling seamless data sharing, virtual inspections, and optimized maintenance planning.
5. What are the key benefits of 3D laser scanning for power plants?
Early fault detection and reduced downtime
Improved asset reliability and equipment life
Enhanced safety through remote inspections
Lower maintenance costs
Accurate data for better decision-making
6. How accurate is 3D laser scanning for industrial maintenance?
3D laser scanning delivers millimeter-level accuracy, capturing up to 2.6 million points per second. This precision helps detect even the smallest structural changes, misalignments, or cracks in plant equipment.
7. Can 3D laser scanning integrate with asset management systems?
Yes. Scan data from TopBIM’s 3D laser scanning solutions can be integrated with EAM, BIM, and GIS platforms, ensuring real-time synchronization between digital models and physical assets for effective maintenance planning.
8. How does 3D laser scanning improve safety in power plants?
By using drones and remote LiDAR systems, 3D laser scanning reduces the need for manual inspections in hazardous or hard-to-reach areas, minimizing safety risks and improving worker protection.
9. What is the difference between preventive and predictive maintenance?
Preventive maintenance follows a fixed schedule, while predictive maintenance relies on real-time data from sensors and 3D scans to determine when equipment actually needs attention — making it more efficient and cost-effective.
10. How can power plants benefit from TopBIM’s 3D scanning services?
With TopBIM’s 3D laser scanning expertise, power plants gain precise digital twins, automated condition monitoring, reduced downtime, improved collaboration, and long-term operational efficiency through predictive asset management.
Further Reading
How to Process Laser Scan Data and Select the Right Scanning Provider or Technology?
Ultimate Guide to 3D Laser Scanning & LiDAR Scanning
Comprehensive Guide on As-Built Surveys
How to Conduct 3D Laser Scanning in Data Centers and Choose the Right Tools?
Comprehensive Guide to 3D Laser Scanning for Power Plants
How to Use As-Built Surveys in Renovation Projects and Avoid Common Mistakes?
How to Conduct an As-Built Survey and Choose the Right Tools for Your Project?
Our Services
Latest Post
Get A Free Quote
BIM Construction is the Future
Building information modeling (BIM) is the future of building design and construction. Get in touch with our BIM Experts.





