Well, looks like we’ve finally found a way to give those old physical buildings a digital makeover with Scan to BIM. This technology allows us to convert real-world structures into 3D models, one scan at a time. Think of it as the ultimate virtual renovation that preserves the essence of old school architecture while bringing it into the 21st century.
Table of Contents
ToggleWho needs blueprints when you’ve got an accurate and precise digital model that captures every nook and cranny?
Plus, with its ability to detect potential structural issues before they become actual problems, Scan to BIM is like having a building therapist that can tell you exactly where it hurts. Say goodbye to tedious measuring and hello to effortless digitization.
Let’s face it – ain’t nobody got time for manual property scanning when there are more exciting things to do like marvel at the beauty of your newly transformed 3D masterpiece!
LiDAR scanning is expanding, and BIM companies have amassed an extensive workforce of BIM Modelers. BIM service providers have extensive training in building design, and the BIM team can transform scans and outdated blueprints into Revit models, enabling accurate detailing of every member of the family and component.
Compared to the traditional method of doing site surveys with your in-house design team, scan to BIM saves time and money. BIM Engineers collaborate with the best laser scanning businesses to create your model quickly and precisely for refurbishment projects.
What are the methodologies to convert physical structures into 3d model?
There are two main methodologies for converting physical structures into 3D models – photogrammetry and 3D laser scanning.
- Photogrammetry uses a series of overlapping photographs to create a 3D model. This is done by taking photographs of the object from multiple angles and then using software to stitch the photographs together. The software creates a point cloud, which is a collection of points in space that represent the object’s surface. The point cloud can then be converted into a 3D model.
- 3D laser scanning uses a laser scanner to create a 3D model. The laser scanner emits a laser beam and measures the time it takes for the beam to reflect back from the object. The scanner then creates a point cloud, which is a collection of points in space that represent the object’s surface. The point cloud can then be converted into a 3D model.
Both photogrammetry and 3D laser scanning can be used to create accurate 3D models of physical structures.
Advantages of photogrammetry:
- Photogrammetry is a non-contact method, so it does not damage the object being scanned.
- Photogrammetry can be used to scan objects that are large or difficult to access.
- Photogrammetry is relatively inexpensive.
Advantages of 3D laser scanning:
- 3D laser scanning is a fast and accurate method.
- 3D laser scanning can be used to scan objects in any lighting condition.
- 3D laser scanning can be used to scan objects that are difficult to access.
Which method is better?
The best method for a particular project will depend on the specific needs of the project. If the object is large or complex, or if it is difficult to access, then 3D laser scanning may be the best option.
Explore Our 3D Laser Scanning High Definition Survey Services
If the object is small or simple, then photogrammetry may be a more cost-effective option. In general, photogrammetry is a good choice for projects where the accuracy of the 3D model is not critical, and where the cost of the project is a major factor.
3D laser scanning is a good choice for projects where the accuracy of the 3D model is critical, and where the cost of the project is not a major factor.
Here is a table that summarizes the differences between photogrammetry and 3D laser scanning:
Feature | Photogrammetry | 3D laser scanning |
Accuracy | Can be less accurate than 3D laser scanning | More accurate than photogrammetry |
Cost | Less expensive | More expensive |
Speed | Can be slower than 3D laser scanning | Faster than photogrammetry |
Access | Can be used to scan objects that are difficult to access | Can be used to scan objects that are difficult to access |
Color and texture | Can capture color and texture information | Cannot capture color or texture information |
Laser Scanning and its Suitable Types
Laser scanning is a technology which allows for the rapid and efficient acquisition of accurate data about an object or environment. This involves using a laser to emit pulses of light, and then measuring the time it takes for those pulses to bounce back to the scanner.
Different types of lasers and scanners can be used for different applications, ranging from capturing precise measurements of individual objects in 3D models, to creating detailed maps of entire buildings or landscapes.
Some common types of laser scanners include:
- Terrestrial scanners, which are typically used for surveying land-based structures with high accuracy
- Airborne LiDAR scanners, which are often used for mapping large areas or capturing topographical data from aircraft
- Handheld 3D scanners, which are smaller devices that can be used for more detailed scans of individual objects or construction sites.
The following categories of 3D scanning technologies can be distinguished based on their underlying physical underpinnings:
- Laser triangulation: This involves projecting a laser beam onto a surface and measuring the laser ray’s distortion.
- Structured Light: When a light pattern is projected onto a surface, structured light analyses how the pattern deforms to produce a three-dimensional scan of the surface’s geometry.
- Photogrammetry: With the aid of computer vision and computational geometry methods, photogrammetry—also known as “3D scan from photographs”—reconstructs a subject in 3D from 2D captures (pictures).
- Contact Based 3D Scanning: Technology for contact-based 3D scanning depends on sampling a number of locations on a surface and measuring those points using a mechanical, optical, or physical probe.
- Laser Pulse 3D Scanning: Based on the Time of Flight (ToF) of a laser beam, a laser pulse. A sensor collects the laser beam after it has been projected onto a surface. The laser’s time of travel between emission and reception provides the 3D scanner with geometrical information about the surface.
What is Scan to BIM?
Scan to BIM is the process by which a real-world object is scanned and turned into a 3D model. Architects and engineers utilize this model to better comprehend the object and produce precise drawings and blueprints. A laser scanner is used in the Scan to BIM method to accurately collect and model a 3D scan of the real-world conditions on your project.
The scan is loaded into a 3D modeling program so that it may either be used to produce an accurate as-built model or to inform the architectural team about the design under precise conditions.
Three crucial steps in 3D Laser scanning procedure
Contractors utilize 3D laser scanning for buildings as a crucial tool since it enables them to produce precise models of existing structures. This is particularly crucial when it comes to historic structures because thorough documentation is crucial.
- Using a 3D laser scanner to get the data
- Returning the data to the design studio
- Applying it to the BIM procedure
As-built drawings, which can be utilized for a number of things including construction planning and quality control, can also be produced using 3D laser scanning. BIM companies supplement existing staff with skilled individuals who can correctly operate, set up, and execute the scan to BIM process.
Scan to BIM Process
Bascially 3D scanning helps BIM engineers to quickly and accurately gather data on the spot. A tripod-mounted 3D laser scanner with an eye-safe laser and rapid rotation is used. When the laser beam strikes a solid surface, a coordinate or point is created to represent the position in relation to the scanner. These points are logged in millions in order to produce an accurate image.
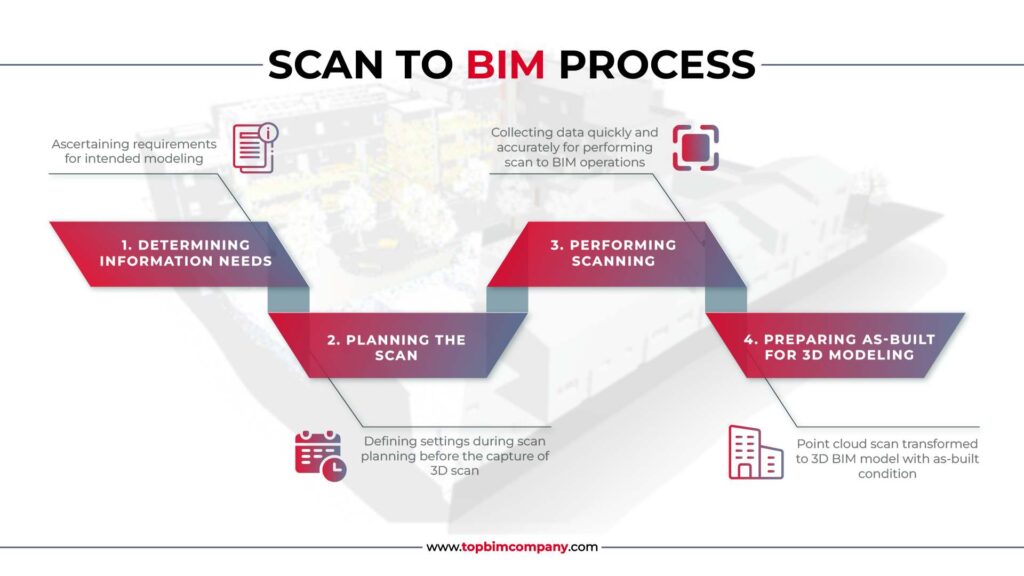
The complete process may be broken down into four stages:
1. Determination of information needs
although It’s crucial to ascertain all the requirements for the intended model/drawings before we start the scan to BIM procedure. The detail in the model should be determined as increased modeling precision enhanced the as-built model BIM’s steadiness for the proposed appliance. Yet, the cost increases with the level of detail. Hence, a trade-off between price and data density must be negotiated.
You can explore our As-Built Drawing Services – how we designed to meet the unique needs of each of our clients, and we work closely with them to ensure that their specific Construction Drawings & Documentation requirements are met.
2. Planned scanning
Prior to the capture of a 3D scan, settings are defined during scan planning. It is vital as it is tricky to place building design documentation that has been accomplished. Hence, optimizing the scanning parameters may be useful. It also determines all properties essential for scanning. The parameter includes coverage in accurate space resolution and other characteristics, such as place, angular resolution, etc.
Our BIM Professionals will provide accurate and quality 3D Digital Models.
3. Performing Scanning
A 3D laser scanner, which gathers data quickly and accurately, is used to perform scan to BIM operations. The apparatus has a fast-rotating, eye-safe laser. When a solid item is detected by the laser beam, its location is immediately recorded as “points,” or coordinates, and the device is frequently mounted on a tripod.
A very accurate digital representation is produced by grouping these points together during mapping. The scanner will colorize all the points after they have been gathered to create a point cloud scan, or 3D depiction of the area from various angles.
The external and interior structure, as well as any hidden mechanical, electrical, plumbing, and fire protection equipment, can be captured using a 3D laser scanner. The scanned data is then converted into a 3D model using the Revit software.
The scanning procedure can also be carried out in a variety of ways, including:
Scans in 360 degrees:
- Time-of-Flight: Every position’s horizontal and vertical angles are measured, requiring the scanner head to occupy every grid position during a scan.
- Phase-based Scans: The sole distinction is that the distance is determined by measuring the phase change of the reflected laser energy.
4. Preparing As-Built for the New-Build 3D Modeling
The collected Point Cloud Scan to BIM data is transformed into a 3D BIM model with the as-built condition of the existing building in the second and last stage of the Scan to BIM process.
- Interpreting the Point Cloud Data: At this stage, scanning software like Autodesk’s Recap is used to analyze the point cloud scan of the building systems. The physical and functional details of each building system are extracted by BIM modelers. The point cloud scan’s numerous viewing points give the structure holistic visibility and guarantee the representation’s accuracy.
- Using a 3D modeling technique: Through 3D modeling, the as-built circumstances of the structure are depicted in the scan. This information is then used for a variety of reasons, such as remodeling, redesigning, and renovating any element of the building. You can have your desired as-built model complete with the necessary building system data, after this last stage of Scan to BIM.
Latest Software and Associated Technologies of 3D Laser Scanning:
Photogrammetry Software:
- 3DF Zephyr
- Agisoft Metashape
- Autodesk ReCap
- Context Capture by Bentley
- Colmap
- Drone Display https://youtu.be/NS8WLnoFqyE
- IMAGINE Photogrammetry: https://youtu.be/cCJgQTUCQYs
- Meshroom:
- MicMac:
- OpenMVG:
- Photomodeler:
- Pix4D:
3D scanning software for 3D scanners:
- Artec Studio: https://youtu.be/k08nbH0MFyY
- PolyWorks:
- Volume Graphics:
Apps for 3D scanning:
- Qlone: https://youtu.be/XkTaCOQ_OjI
- Trnio:
- Sony 3D Creator:
- Heges:
- Scann3D:
- 3D Creator: https://youtu.be/V4qZcNZhD28
- Scandy Pro 3D Scanner:
To get a detailed overview of latest software and associated technologies of 3D Laser scanning, check out our blog – “Latest Software Applications & Technologies of 3D Laser Scanning”
Points to consider while implementing best Scan-to-BIM practices
Here are some points to consider while implementing best Scan-to-BIM practices:
- Define the scope of work: The first step is to define the scope of work for the scan-to-BIM project. This includes identifying the areas that need to be scanned, the level of detail required, and the desired output.
- Choose the right laser scanner: There are a variety of laser scanners available, so it is important to choose the right one for the project. The scanner should be able to capture the required level of detail and accuracy, and it should be compatible with the software that will be used to process the data.
- Plan the scan: Once the laser scanner has been chosen, it is important to plan the scan. This includes determining the best scanning locations, the scanning sequence, and the number of scans required.
- Gather the data: The next step is data collection. This involves setting up the laser scanner, scanning the desired areas, and post-processing of the data.
- Process the data: The data collected from the laser scanner needs to be processed in order to create a 3D point cloud. This process involves removing noise, filtering the data, and registering the scans.
- Create the BIM model: The final step is to create the BIM model. This involves importing the point cloud into BIM software and using the data to create the model.
Here are some additional best practices to consider:
- Use a qualified team: The scan-to-BIM process should be carried out by a qualified team that has experience with 3D laser scanning and BIM.
- Use the right software: The right software is essential for the scan-to-BIM process. The software should be able to process the data accurately and create a high-quality BIM model.
- Document the process: The scan-to-BIM process should be documented in order to track the progress of the project and ensure that the results are accurate.
By following these best practices, you can ensure that the scan-to-BIM process is successful and that you get the results you need.
Future of Converting Buildings into 3D Models with Scan to BIM
The future of converting physical buildings into 3D models using Scan to BIM process is promising and expected to play a significant role in the AEC industry.
Scan to BIM process captures a space with a laser scanner and turns it into a 3D digital model for planning building environment. The model can be used for building conservation, renovation projects, retrofitting, and planning new constructions.
The accuracy of the Bill of Material created with Scan to BIM data reduces the likelihood of building budget overruns. To create an as-built model for facility management, maintenance, and operations, BIM models from laser-scanned data are used.
As technology advances, software tools get more sophisticated, enabling faster processing times that create high-quality outputs in record time.
This trend will continue as virtual reality aids the process by creating immersive environments that allow stakeholders to experience the building’s potential before starting work.
Additionally, as sustainability concerns grow in importance for all industries, utilizing existing structures through retrofitting becomes vital. Thus it seems clear that the use of scan-to-BIM with increased flexibility and convenience will become a standard industry practice across domains making it essential for professionals to adopt this skill set.
Implement scan to BIM in your project workflow and get improved accuracy and smarter judgment
You may also like to read:
- Automate Point Cloud To 3D Model Creation: AI & ML
- Revolutionizing Building Construction 3D Laser Scanning Technology
- Virtual Design & Construction (VDC): Enhance Project Efficiency & Collaboration
Our Services
Latest Post
Get A Free Quote
BIM Construction is the Future
Building information modeling (BIM) is the future of building design and construction. Get in touch with our BIM Experts.