Virtual Design and Construction is like having a virtual magic bookmark for your construction project. It’s the process of creating a 3D model of your planned structure, then simulating everything from material selection to construction sequencing to ensure a smooth and efficient build.
Table of Contents
ToggleVDC uses advanced technology such as Building Information Modeling (BIM), 3D laser scanning, and augmented reality to bring your design to life before breaking ground. Combining BIM and PPM – an adequate work and management scheme, VDC supports construction professionals, in an integrated and simultaneous way.
With VDC, you can experiment with designs without wasting any materials or labor hours, work collaboratively with stakeholders involved, reduce overall costs, and even increase sustainability.
Researchers at the Centre for Integrated Facility Engineering (CIFE) of Stanford University created VDC in 2001. CIFE has been working to improve the way the AEC sector plans, conceptualizes, and carries out design and construction since the late 1980s. One of CIFE’s most notable technologies, VDC, has now been at the forefront of tackling the productivity issue in construction.
Workflow of VDC
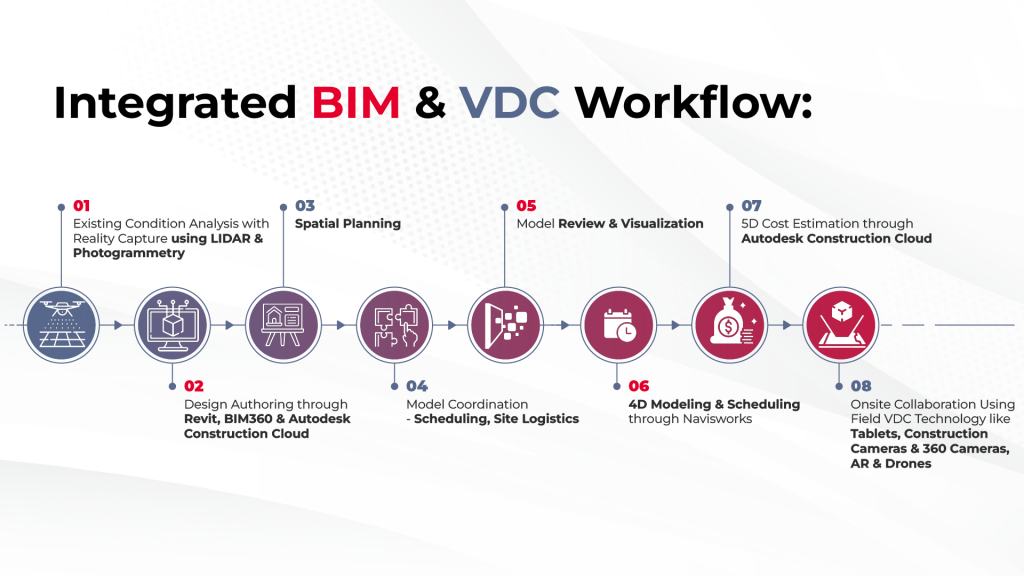
VDC Workflow and Process, or Virtual Design and Construction Workflow and Process, is a comprehensive term framework used to describe the entire process flow of building design and construction.
This methodology enables a collaborative approach that involves stakeholders in the project such as architects, engineers, contractors, and owners. The VDC workflow utilizes multiple tools and technologies to create an integrated platform that supports efficient communication.
These tools include 3D modeling software such as Revit, advanced BIM systems for virtual designing and testing, and cloud-based communication platforms like Bluebeam or Procore which facilitate real-time collaboration with team members.
Structure of VDC
The structure of Virtual Design and Construction involves integrating various methodologies and concepts to achieve efficient project delivery.
Here is how Integrated Concurrent Engineering (ICE), Project Production Management (PPM), Building Information Modeling (BIM), and Metrics fit within the VDC framework:
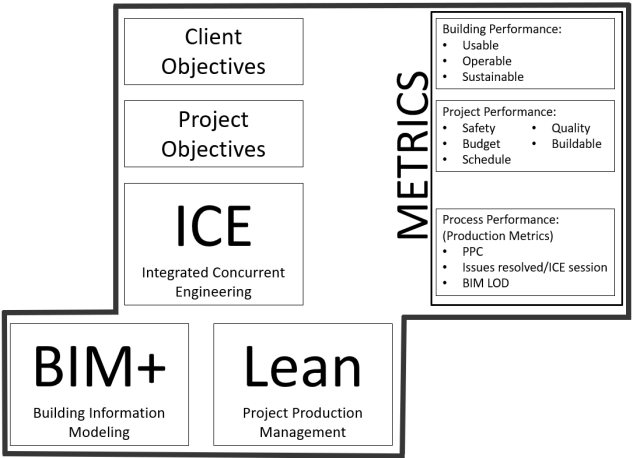
Integrated Concurrent Engineering (ICE)
Integrated Concurrent Engineering is a collaborative approach that involves multidisciplinary teams working together from the early stages of a project. It aims to optimize the design and construction process by integrating the knowledge and expertise of all stakeholders, including architects, engineers, contractors, and suppliers.
ICE promotes concurrent decision-making, information sharing, and continuous feedback loops to improve project outcomes and reduce conflicts.
Project Production Management (PPM)
Project Production Management focuses on managing the production process of a construction project.
It emphasizes the use of production principles and methodologies, such as Lean Construction and Last Planner System, to improve efficiency, reduce waste, and enhance project performance.
PPM involves detailed planning, scheduling, and control of project activities, as well as continuous monitoring, measurement, and improvement of production processes.
Building Information Modeling (BIM)
BIM is a digital depiction of the physical and functional attributes of a construction project. The technology involves creating and managing a 3D model that integrates all relevant project data, including geometry, materials, quantities, and performance information.
BIM facilitates collaboration, visualization, and analysis throughout the project lifecycle. It supports clash detection, coordination, design optimization, and simulation, enabling stakeholders to make informed decisions and improve project coordination and efficiency.
Metrics
Metrics play a crucial role in VDC by providing quantitative measures to evaluate project performance, track progress, and identify areas for improvement.
These metrics can include various key performance indicators (KPIs) related to cost, schedule, quality, safety, and sustainability. Metrics help project teams assess their performance against project objectives, benchmarks, or industry standards.
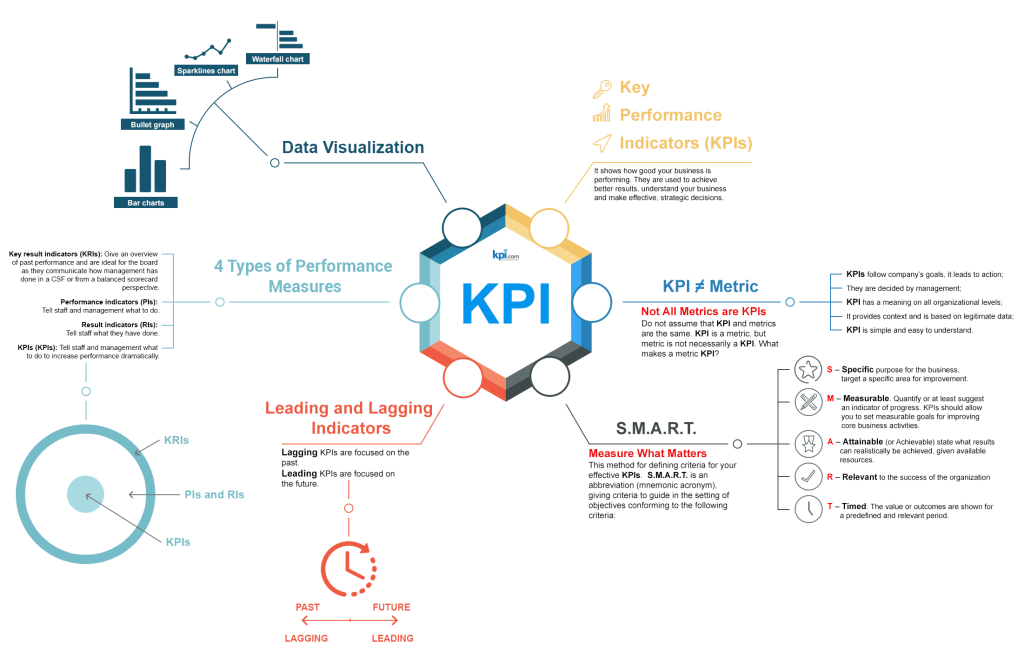
By analyzing metrics, project stakeholders can make data-driven decisions, identify bottlenecks, and implement corrective actions to optimize project outcomes.
In the VDC structure, these components are interconnected and mutually reinforce each other. Integrated Concurrent Engineering promotes collaboration and knowledge sharing, Project Production Management focuses on efficient production processes, Building Information Modeling provides a digital representation and facilitates coordination, and Metrics provide a means to measure and evaluate project performance.
Together, they contribute to a comprehensive and systematic approach to project delivery, resulting in improved efficiency, cost-effectiveness, and overall project success.
How Associated Tools & Technologies Help in executing the workflow?
Virtual Design and Construction relies on various tools and technologies to enhance collaboration, streamline project workflows, and improve project outcomes. Here are some commonly used tools and technologies in VDC:
Building Information Modeling (BIM) Software
BIM software platforms like Autodesk Revit, Bentley MicroStation, and ArchiCAD are at the core of VDC. They enable the creation of intelligent 3D models that integrate various building components and provide data-rich information throughout the project lifecycle.
Clash Coordination Software
Tools like Navisworks, Solibri, and BIM Track facilitate clash detection and coordination among different building systems and disciplines. They help identify and resolve clashes or conflicts between structural, architectural, MEP (mechanical, electrical, plumbing) systems, reducing rework and coordination issues.
4D/5D Construction Simulation
4D simulation software, such as Synchro, provides a visual representation of the project timeline by integrating the BIM model with the construction schedule. It enables project teams to visualize the construction sequence and identify potential scheduling conflicts or resource constraints. Additionally, 5D simulation tools integrate cost data into the model, enabling cost estimation and analysis.
Laser Scanning and Reality Capture
Laser scanning technologies, such as LiDAR (Light Detection and Ranging), enable the accurate capture of existing site conditions. These scans can be used to create point clouds or 3D models that can be integrated with BIM, allowing for clash detection, accurate measurements, and improved as-built documentation.
Virtual Reality (VR) and Augmented Reality (AR)
VR and AR technologies provide immersive experiences and aid in design visualization, coordination, and communication.
Tools like
Enable stakeholders to experience the project virtually, assess spatial relationships, and make informed decisions.
Cloud Collaboration and Project Management
Cloud-based platforms like Autodesk BIM 360, Procore, and Trimble Connect facilitate real-time collaboration, document sharing, and project management. They allow project teams to access the latest project information, streamline communication, and manage project documentation efficiently.
Computational Design and Parametric Modeling
Tools like
Grasshopper (for Rhino),
Dynamo (for Revit),
Generative Components (for Bentley)
enable computational design and parametric modeling. These tools automate design processes, create complex geometries, optimize performance parameters, and facilitate design exploration.
Mobile Applications
Mobile apps like Fieldwire, PlanGrid, and Bluebeam Revu provide on-site access to project information, drawings, and documents. They enable efficient communication, issue tracking, and field data collection, improving construction coordination and reducing errors.
Data Analytics and Artificial Intelligence (AI)
Data analytics and AI technologies help extract insights from project data. They can be used to analyze performance metrics, optimize energy usage, predict construction schedules, and make informed decisions based on historical data.
What are the Applications & Associated Benefits of VDC?
Virtual Design and Construction has numerous applications in the architectural, engineering, and construction (AEC) industry. Here are some key areas where VDC is widely utilized and benefit AEC Professionals:
Design Visualization
VDC enables architects, engineers, and clients to visualize and assess design concepts in a virtual environment before construction begins. It helps stakeholders understand spatial relationships, aesthetics, and functionality, facilitating better design decision-making.
Clash Detection and Coordination
VDC allows for clash detection and coordination among different building systems and disciplines, such as architectural, structural, mechanical, electrical, and plumbing. Clash detection tools integrated with BIM models identify conflicts early on, minimizing rework, cost overruns, and construction delays.
Construction Simulation and Sequencing
VDC incorporates 4D and 5D construction simulation, linking the BIM model with project schedules and cost data. This integration provides a visual representation of the construction sequence and enables stakeholders to assess the impact of scheduling changes, optimize resource allocation, and improve project planning.
Quantity Takeoff and Cost Estimation
VDC supports accurate quantity takeoff and cost estimation by extracting information from BIM models. Quantities of materials and components can be automatically calculated, enabling faster and more accurate cost estimating, procurement planning, and budgeting.
Prefabrication and Modular Construction
VDC facilitates off-site prefabrication and modular construction processes. BIM models can be utilized to design and fabricate building components with precision, reducing waste, improving quality control, and expediting construction timelines.
Facility Management and Operations
VDC extends its benefits beyond the construction phase by integrating BIM models with facility management systems. This allows owners and facility managers to access asset information, maintenance schedules, and equipment specifications, enhancing the efficiency of facility operations and maintenance activities.
Collaboration and Communication
VDC improves collaboration and communication among project stakeholders by providing a shared, digital platform for information exchange. Real-time access to BIM models, project documentation, and communication tools enables effective coordination, reduces errors, and facilitates better decision-making.
Sustainable Design and Analysis
VDC supports sustainable design practices by integrating energy analysis, daylighting simulation, and other performance metrics within the BIM environment. This enables designers to assess and optimize energy efficiency, thermal comfort, and environmental performance during the design phase itself.
Risk Management and Safety Planning
VDC can be utilized for risk management and safety planning. By simulating construction activities, identifying potential hazards, and evaluating safety measures, project teams can proactively address safety concerns and minimize on-site accidents.
As-Built Documentation
VDC assists in generating accurate as-built documentation by capturing and recording changes made during construction. This documentation serves as a valuable reference for future renovations, maintenance, and facility management.
These applications highlight the diverse ways in which VDC enhances collaboration, coordination, efficiency, and quality throughout the entire project lifecycle in the AEC industry.
Challenges and Implementation Strategies for VDC
Implementing Virtual Design and Construction in an organization can bring several benefits, but it also comes with its own set of challenges. Here are some common challenges and strategies for successful implementation:
Misperception that information must be restricted
There might be a reluctance to share information openly due to concerns about intellectual property or competitive advantage.
To overcome this challenge, organizations should emphasize the importance of collaboration, trust, and the collective benefits of information sharing. Clear guidelines and agreements on data ownership and sharing can help address these concerns.
Traditions have deep roots, and change is tough
The construction industry is known for its traditional practices and resistance to change.
To overcome this challenge, organizations should focus on creating a culture of innovation and continuous improvement. Leadership support, training programs, and communication about the benefits of VDC can help overcome resistance and foster a more receptive mindset.
Engagement is easy, continuous engagement is hard
Initial engagement and enthusiasm for VDC may wane over time if there is a lack of ongoing support and reinforcement.
It is crucial to establish a structured approach for continuous engagement, including regular training, knowledge sharing sessions, and feedback loops. Involving employees in the decision-making process and showcasing success stories can help maintain enthusiasm and commitment.
Your business will have greater visibility into each project
With VDC, there is increased transparency and visibility into project data and progress. However, managing and leveraging this increased visibility can be challenging.
Organizations should establish data governance policies, define clear roles and responsibilities, and implement robust project management practices to effectively utilize the available data and ensure it aligns with business objectives.
Your business will be involved much earlier in each project
VDC enables early involvement in the project lifecycle, starting from concept and design stages. This requires a shift in traditional workflows and collaboration practices.
Organizations should establish cross-functional teams and encourage early involvement of all stakeholders, including architects, engineers, contractors, and clients. Clear communication channels and processes for early-stage collaboration will be essential.
Your team will need to develop new skills
VDC requires new skills and competencies in areas such as BIM modeling, clash detection, construction simulation, and data analysis.
Organizations should invest in training programs and provide professional development opportunities to upskill their workforce. Collaboration with external experts, attending industry conferences, and leveraging online learning resources can also aid in developing the necessary skills.
By addressing these challenges and implementing effective strategies, organizations can successfully adopt VDC and harness its benefits, leading to improved project outcomes, enhanced collaboration, and increased efficiency in the AEC industry.
You may also like to read:
12 Construction Industry Trends To Watch [2023-2030]
BIM LOD (Level Of Development)- 100 200 300 350 400 500
Future of BIM Construction Trends
Innovative BIM Modeling Trends Shaping AEC Industry
Construction Industry Trends to Watch 2023
Role of Autodesk in Future Construction Technology
3D Scanning Of Buildings for Architecture, Engineering, & Construction (AEC)
5 Ways of Improving the Value of BIM Objects
Commonly used terms related to VDC
What is a CDE (Common Data Environment)?
A Common Data Environment is a centralized platform or system that allows project stakeholders to access, share, and manage project-related information and documents.
It serves as a single source of truth for project data, ensuring that all stakeholders have access to the most up-to-date information. A CDE is a key component of effective collaboration and information management in VDC.
What are IFC (Industry Foundation Classes)?
Industry Foundation Classes (IFC) is an open standard file format used for exchanging and sharing BIM data between different software applications. IFC files contain information about building elements, their properties, relationships, and spatial coordinates.
The IFC format enables interoperability and seamless exchange of BIM data across different software platforms, promoting collaboration and data consistency in VDC.
What’s the difference between VDC and BIM?
VDC (Virtual Design and Construction) is a broader concept that encompasses the use of various technologies, processes, and methodologies to improve project outcomes.
It includes elements such as BIM (Building Information Modeling), clash detection, construction simulation, and project management.
BIM, on the other hand, specifically refers to the creation and management of digital 3D models that contain information about the physical and functional characteristics of a building. BIM is a fundamental component of VDC, as it provides the basis for data integration, coordination, and visualization throughout the project lifecycle.
How does AEC (Architecture, Engineering, and Construction) help VDC Coordinators?
The AEC industry plays a crucial role in supporting VDC Coordinators in various ways:
- Expertise and Experience: AEC professionals bring their domain expertise and experience in architectural design, engineering, and construction to the VDC coordination process. They provide valuable insights and knowledge in planning, designing, and implementing VDC strategies.
- Collaboration and Communication: AEC professionals collaborate closely with VDC Coordinators to ensure effective communication and coordination among project stakeholders. They help translate design and construction requirements into actionable plans and facilitate smooth information flow.
- Technical Support: AEC professionals contribute to the technical aspects of VDC implementation, such as BIM modeling, clash detection, and construction sequencing. They assist VDC Coordinators in utilizing software tools and technologies effectively to achieve project goals.
- Quality Control: AEC professionals help ensure the quality and accuracy of BIM models, construction documentation, and project deliverables. They review designs, specifications, and construction plans to identify potential issues and provide recommendations for improvement.
Overall, AEC professionals collaborate with VDC Coordinators to leverage their expertise, promote best practices, and ensure successful implementation of VDC strategies in construction projects.

Extract quantities for costing and managerial management.
To know more about how we can help you improving your project cost efficacy
Our Services
Latest Post
Get A Free Quote
BIM Construction is the Future
Building information modeling (BIM) is the future of building design and construction. Get in touch with our BIM Experts.