Transport is an important infrastructure. To felicitate our daily travel needs and logistics for city’s economics, there has to be a thoughtful transport planning for making our surroundings more liveable. However, the catch here is that the transport infrastructural planning needs development tuned to population projection and geological data. This emphasizes the need of a data-driven backend that could propel transport planning in a right direction.
Table of Contents
ToggleThis data-driven backend could be GIS (Geographic Information System). GIS is a set of tools that aims to analyze geographical mapping data for multiple applications.
How actually GIS could aid transportation infrastructure and planning
GIS is a type of information system used for reporting, managing, and analyzing geographic data. With its capacity to store vast volumes of data and provide personalized cartographic outputs, it has completely changed geography. Transportation-related problems, in particular GIS-T, are innovative applications since they depend on analytical techniques and visualization.
Three kinds of subjects may be used to facilitate and improve transportation studies, while two complementary approaches to GIS-T study are to enhance GIS for transportation applications.
Representations of data – How different transport system components—including the network and their technical and operational attributes (capacity, speed)—are represented as a database.
Modeling and analysis – How real-world transportation activity may be modeled using transport techniques.
Utilization – Which kinds of applications work best with the data and analytical powers of GIS-T.
GIS-T Data Representations
GIS research integrates geographical and non-spatial data to solve real-world problems. Field-based and object-based data models are used, representing geographic space as discrete objects or continuous combinations of real-world characteristics.
GIS-T research uses object-based and field-based models, with field-based models better for linearly referenced data and object-based models for network research.
GIS-T software has developed enterprise and multidimensional models for transportation-related applications, combining temporal, 2-D, 3-D, and 1-D data.
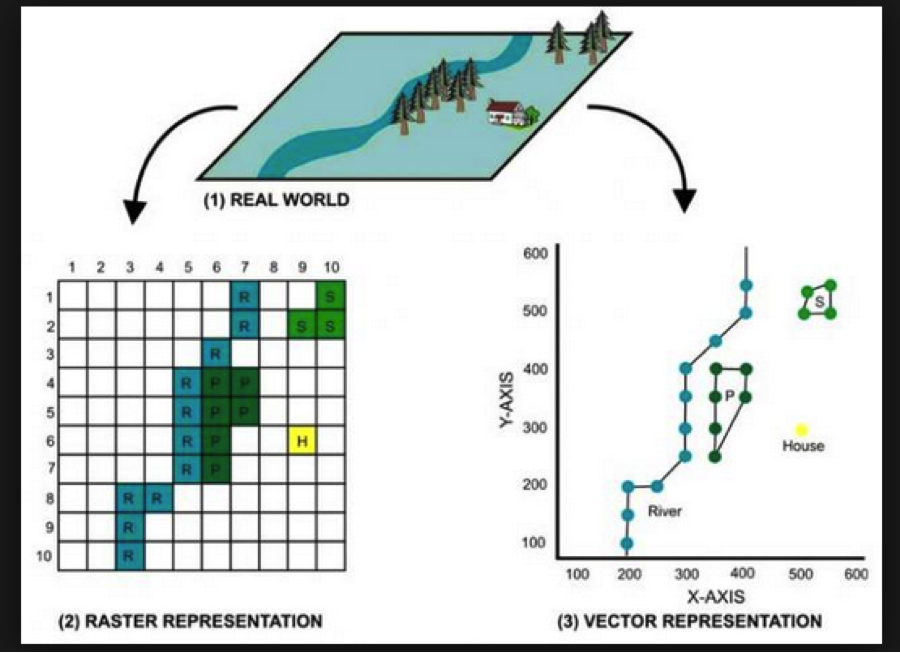
Image source: gis.stackexchange.com
Cloud computing applications simplify system design and storage. Location-aware technology enables large-scale data gathering, creating new challenges in GIS-T research. GIS-T is essential for efficient transportation data expression.
GIS-T Analysis and Modeling

GIS-T applications use standard GIS functions for data management, analysis, and visualization, but transportation has developed unique analysis methods and models. Commercial GIS software offers basic procedures, but travel demand models are only available in select packages. Understanding these methods improves GIS-T design and analysis capabilities.
GIS-T applications
In the fields of logistics and transportation, GIS-T applications play a critical role in
- Routing
- Vehicle tracking
- Fleet management
- Site selection
- Infrastructure planning
- Economic impact assessment, safety analysis
- Travel demand analysis
- Traffic monitoring
- Public transit planning
Different application demands are addressed by research on multidimensional and enterprise GIS-T data models. There are many uses for driving instructions and logistics as a result of the Internet’s and cellular communications’ explosive expansion. Following are the applications of GIS in transportation planning explained in detail –
Also Read – GIS Mapping Software For Construction Industry
Infrastructure Maintenance and management
The magnified GPS images coupled with GIS could provide real time performance insights on the infrastructure developed. Transportation infrastructural assets like highways and roads have heavy budgets to be take care of. With precise usage and condition imageries coupled up with predicted usage data, government authorities with stakeholders can better upgrade the infrastructure.
- The whole cycle to infrastructure management and maintenance looks like –
- Generating the real-time asset performance with accurate public felicitation imagery data
- Assessment of its current condition which is its physical appearance and renewal needs
- Performance projection based on population increment and current structural conditions
- Devising predictive maintenance based on the critical performance metrics
Accident response measures
The arrival of data-driven AEC tools has ensured that nothing is done on assumptions. Same is the intention with utilizing GIS on design dashboard, through GIS each of the event occurrence can be analysed better. Also, GIS aids in accident reporting by pinpointing accident locations and contributing to quick emergency responses.
- Integrating GIS with BIM dashboard is intended towards minimizing the unfortunate incidents. However, even if the accident occurs GIS aids in –
- Identifying the exact location and root cause of the incident
- Running multiple simulation on predicted solutions
- Then finally couple solutions with user behaviour to derive a final optimal development
Optimized route planning
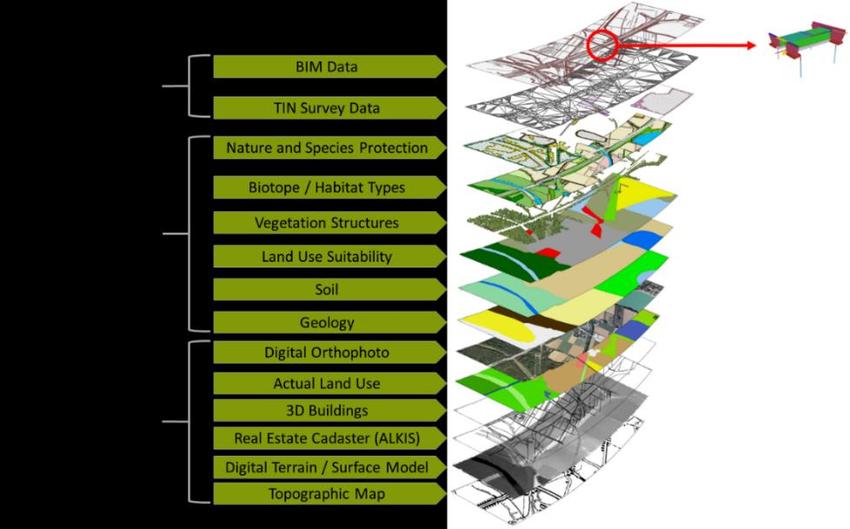
Image Source: Researchgate
The best argument in the favour of BIM-GIS integrated workflow for transportation planning would be intelligent traffic simulation. Recorded traffic behaviours over a period of time can provide data to predictive AI-systems to have a slate for planning routes. This specific approach can help in improving traffic flow, reduction in transportation bottlenecks, and transportation infrastructure design enhancement.
GIS aids in –
- Route accessibility data analysis
- Plugging in with real-time GIS and rich demographic data
- Devising optimized route design
Environmental Impact Assessment
GIS data is all about geographic data i.e., the physical and vegetative land data. The linear sustainable approach gets it all wrong with a primary focus on climatic data only. With a GIS development approach, the final output can actually respect the land topography causing a minimal impact on the environment. Even the green land restoration necessary in parallel to infrastructure development, could be fasten up with GIS. The GIS for Environmental Impact Assessment (EIA) can have following applications –
- Rehabilitation – The rebuilding preparedness with transportation infrastructure when disaster occurs
- Green land conservation – Optimizing the transportation design in such a way that it minimizes the impact on land topography
- Sustainable transport infrastructure – Democratizing a thoughtful public transport system, reducing individual carbon foot print
Logistics management
The GIS is a binding thread for all mode of transportation. Right from probing into intersection challenges for optimized fleet management and cargo monitoring to planning of transportation hubs, GIS take care of all.
For an economy to properly faction, logistics has to be smooth and that could only be achievable by Organisation of information for each of the stakeholders participating in the activities. The whole logistics management with GIS will look like –
- Identifying suitable locations for transportation hubs, incentivizing productivity throughout logistics
- Real time vehicle monitoring with introspection on critical metrics for performance
- Combining the GIS data with ERP of requirements for developing a comprehensive logistics layout
Use cases of GIS applications in solving transportation infrastructure bottlenecks
Below are some of the examples on how GIS applications has been deployed to solve the transportation and associated infrastructure issues –
See the performance
Due to the internet’s explosive expansion, several GIS-T applications have emerged. One such application is driving instructions, which are being utilized more and more in the business sector for logistics.
Work together and communicate
The ArcGIS platform increases public trust in strategic, economical decision-making and promotes organizational collaboration, both of which are beneficial for effective transportation planning. By demonstrating the road and highway designs’ efficacy, it increases public support.
Transportation Planning with Urban SDK
To increase bicycle safety, Palm Beach County, Florida is putting smart city planning into practice. Planners can turn big information into a tool that’s easy to use by utilizing Urban SDK’s GIS Studio. Plotting data from 2019 to 2021 on roads, traffic, bike lanes, and accidents, the tool highlights regions with a high number of accidents. Road safety may be given priority by planners, who can also utilize filters to find characteristics that influence accidents and enhance long-term design.
Transparency with Public Dashboards
After cooperation, the public dashboard of the Urban SDK streamlines data sharing by minimizing digital clutter and preventing email searches. It enables coordinated, business-like data exchange without the need for a special program or account. Users may interact, see, and download data from the dashboard without requiring an account or any special software by customizing it with their organization’s logo.
Comprehensive Planning Platform
By enabling the sharing and accessibility of digital data, Urban SDK Studio simplifies planning procedures. It helps with corridor studies, long-term transportation, and city conceptualization, empowering stakeholders to design more intelligent plans and cities.
Challenges when using GIS in transportation
GIS in transportation confronts a number of difficulties, including data availability and quality, system integration, and the requirement for substantial resources. It restricts the inability for efficient utilization and seamless tool integration.
The future of GIS in transportation infrastructure design and planning
With the arrival of LLM trends, there is a high probability of narrow solutions in GIS market too. These solutions might make software more predictive and automated with smart organization of the operations.
Also, the support of increased file interoperability within the industry will ensure more metrics to better the data we would be extracting out of these GIS systems. Therefore, the future of GIS for transport planning is surely positive with more critical metrics and automated comprehension to come.
Further Reading
GIS For Disaster Management
Best GIS Mapping Software And Tools For Construction
Our Services
Latest Post
Get A Free Quote
BIM Construction is the Future
Building information modeling (BIM) is the future of building design and construction. Get in touch with our BIM Experts.