In an era heavily reliant on automation and technology, the importance of Indoor Air Quality (IAQ) as a pivotal performance metric for building systems cannot be overstated.
Table of Contents
ToggleWhile indoor spaces serve as sanctuaries, offering shelter and comfort, the often-neglected factor is the quality of the air we respire within these spaces.
You would like to Explore our – facility management services
Complex heavy HVAC systems should incorporate features to have a probe into IAQ in the age of AI, as natural ventilation proves insufficient for tall and intricate buildings.
IAQ pertains to the state of the air within structures and buildings, influencing the well-being and contentment of their occupants.
This discussion delves comprehensively into the significance of IAQ, encompassing aspects such as air pollutants, their impact on health, regulatory frameworks, evaluation techniques, strategies for enhancement, management protocols, and the prospective landscape of IAQ.
The need for facility management becomes imperative in ensuring optimal IAQ. Facility managers play a vital role in upholding IAQ standards, orchestrating proactive measures, and leveraging real-time data to create healthier and more comfortable indoor environments.
Understanding Indoor Air Pollutants
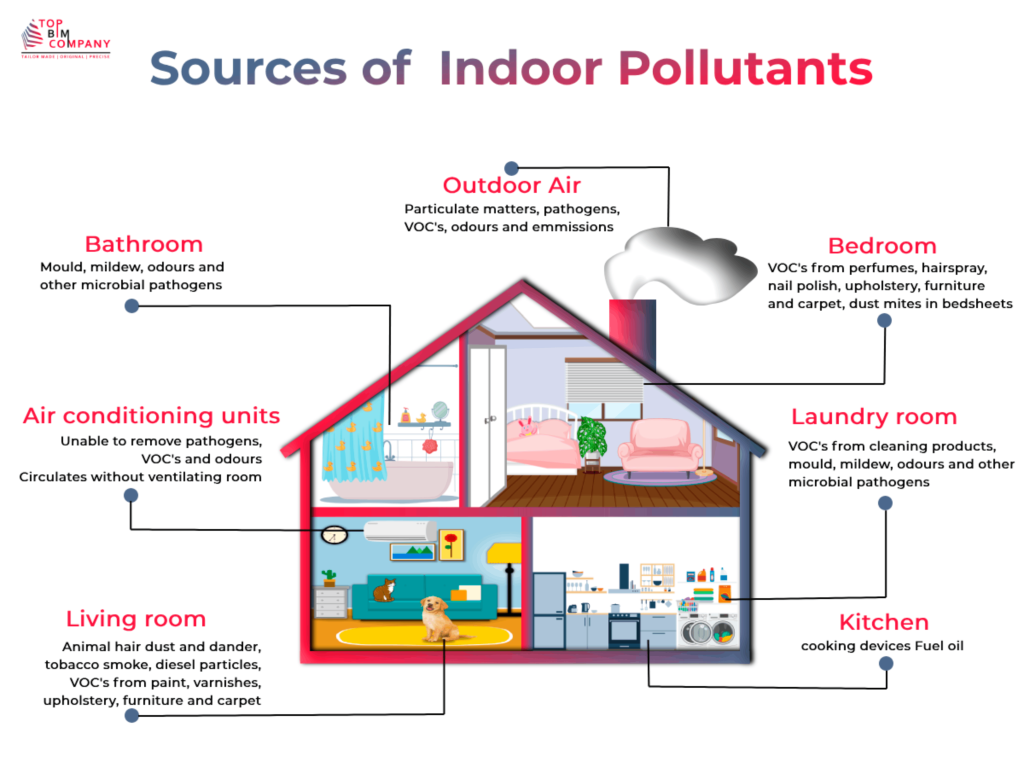
- Common Indoor Air Pollutants: Indoor air pollutants come in various forms, including volatile organic compounds (VOCs), formaldehyde, particulate matter, radon, carbon monoxide, and biological contaminants like mold and bacteria.
- Sources and Causes of Indoor Air Pollutants: These pollutants originate from diverse sources such as building materials, household products, cleaning agents, heating systems, cooking appliances, and even personal activities like smoking. Poor ventilation can also lead to the accumulation of these pollutants.
Health Impacts of Poor IAQ
In the realm of health consequences stemming from inadequate indoor air quality (IAQ), short-term ramifications encompass ailments like headaches, fatigue, dizziness, eye irritation, and allergic responses.
On a more eduring horizon, prolonged exposure to indoor pollutants correlates with graver health implications including respiratory disorders, cardiovascular complications, and even specific forms of cancer.
Notably, vulnerable segments of the population including children, the elderly, pregnant women, and those with preexisting health conditions face heightened susceptibility to the detrimental impact of subpar IAQ.
Air Pollution Impact |
|
Indoor Pollutants: |
|
The process of improving IAQ
Assessing and Monitoring IAQ
- IAQ Testing and Monitoring Methods: Comprehensive IAQ assessments involve the application of testing techniques for specific pollutants along with the measurement of factors like temperature, humidity, and ventilation rates. Methods include air sampling, surface swabs, and real-time monitoring.
- Implementing IAQ Assessments in Facilities: Facility managers can seamlessly integrate regular IAQ assessments into their maintenance routines, aligning with a set of well-defined IAQ metrics. By continuously monitoring metrics such as levels of volatile organic compounds (VOCs), particulate matter, humidity, and ventilation rates, potential concerns can be swiftly identified. This proactive approach ensures that corrective actions are taken promptly, guaranteeing a healthier and more comfortable environment for building occupants.
Maintaining Regulations and Standards for IAQ
- National and International Guidelines: Internationally recognized bodies such as the World Health Organization (WHO) and the Environmental Protection Agency (EPA) have formulated guidelines and standards to uphold acceptable levels of IAQ. These guidelines provide a baseline for maintaining a healthy indoor environment.
- Compliance Requirements for Facilities: Facilities are mandated to conform to these IAQ standards to ensure the well-being of occupants. Non-compliance can result in penalties and legal ramifications, underscoring the necessity of meeting these regulations.
Implementing IAQ Management Programs
- Developing an IAQ Management Policy: Crafting a comprehensive IAQ management policy involves defining objectives, allocating responsibilities, and establishing procedures for sustaining and enhancing IAQ. A well-defined policy forms the foundation for effective IAQ management.
- Steps of Implementing IAQ Programs: Executing IAQ management programs necessitates collaboration among facility managers, occupants, and potentially IAQ professionals. Clear communication, continuous education, and structured training are essential components of successful implementation.
- Better Visualization with BIM: Implementing an IAQ Management Program infused with BIM heralds a new era of superior visualization. Seamlessly integrating 3D modeling and 4D scheduling, BIM offers a comprehensive view of projects, fostering better planning and execution. Smart parameter utilization ensures precise material allocation with 5D, optimizing resources for efficient outcomes. Beyond visualization, BIM empowers asset data management, encapsulating a holistic project lifecycle perspective. Embracing BIM-integrated Facility Management further enhances this journey, where innovation and practicality converge for unparalleled project success.
Improving Indoor Air Quality
- Strategies for Enhancing IAQ: Employing effective ventilation systems, opting for low-VOC (volatile organic compound) building materials, and practicing safe storage of chemicals constitute effective strategies to mitigate indoor air pollutants. These measures actively work towards maintaining cleaner indoor air.
- HVAC System Maintenance and IAQ: Routine maintenance of HVAC systems is pivotal in preventing the accumulation and circulation of dust, mold, and contaminants. Proper care ensures that these systems contribute positively to IAQ.
- Indoor Plants and IAQ: Select indoor plants can serve as natural air purifiers, absorbing pollutants and releasing oxygen. Introducing such greenery contributes to the overall improvement of IAQ.
- Elevating Indoor Air Quality through BIM: Building Information Modeling introduces transformative approaches like Scan to BIM and robust facility data management to enhance IAQ. With Scan to BIM, existing structures are digitally converted into precise 3D models, aiding in predicting ventilation patterns and optimizing air circulation. Integrated facility data management empowers proactive IAQ management by centralizing information on systems and maintenance schedules. BIM’s synergy with IAQ bridges real-world data and digital insights as well as ensures healthier indoor environments.
By following this strategic process, building owners, facility managers, and occupants can collaboratively take substantial steps to elevate IAQ levels.
Adhering to regulations, conducting thorough assessments, employing effective strategies, and implementing management programs all contribute to fostering healthier and more comfortable indoor environments.
American Society of Heating, Refrigerating and Air-Conditioning Engineers (ASHRAE) | Reports that buildings that have undergone thorough IAQ management programs have shown up to a 40% improvement in overall occupant comfort levels. |
How IOT Integrated BIM Facility Management Addresses IAQ Concerns?
- Smart Design with BIM: Building Information Modeling ushers in a new era of design precision. It facilitates the integration of IAQ considerations right from the blueprint phase, optimizing ventilation, and material selection to enhance air quality.
- Real-Time Monitoring with IoT: The Internet of Things (IoT) complements BIM by enabling real-time IAQ data collection through interconnected sensors. This synergy empowers Facility Managers with accurate insights, allowing immediate adjustments to maintain optimal air quality.
- Predictive Analysis: The amalgamation of BIM and IoT opens doors to predictive analysis. This forward-thinking approach anticipates IAQ challenges, enabling proactive measures for enhanced air quality and occupant comfort.
- Data-Driven Decisions: Facility Managers armed with IAQ data make informed decisions, optimizing ventilation systems, and deploying strategies that positively impact both health and energy efficiency.
- Healthier Environments: This integrated approach can lead to healthier indoor spaces, minimizing health risks associated with poor IAQ. It transforms buildings into environments that nurture well-being and productivity.
The Future of IAQ
The possible future of monitoring Indoor Air Quality (IAQ) lies in the convergence of Building Information Modeling (BIM) and the Internet of Things (IoT).
Also Read Complete Guide – Introduction of BIM
BIM offers a comprehensive digital representation of buildings, enabling the integration of IAQ-related data into the facility management stage, while IoT facilitates real-time data collection through interconnected sensors and devices.
Sensors can provide real-time data on IAQ factors, enhancing the accuracy of BIM design implementations. This synergy between BIM and IoT could revolutionize IAQ management, allowing for predictive analysis, instant adjustments to ventilation systems, and data-driven decision-making for optimal air quality.
Ultimately, this integration has the potential to create healthier indoor environments while maximizing energy efficiency and occupant well-being.
You may also like to read:
- BIM in Asset Management: Adoption, Benefits & Differences
Best GIS Mapping Softwares for Construction Industry
Autodesk BIM Batch Suite 2024 | New Features & Benefits - BIM Management- Building Construction Process For General Contractors
- 4 Stages of BIM Process in Building Construction
- Benefits and Role of BIM Design in Construction
- BIM Integrated As-Built Drawings for Building Construction Management
- 5 Ways of Improving the Value of BIM Objects

Want to know more about the benefits of BIM in facility management
Contact TopBIM consultants at preconstruction!
Our Services
Latest Post
Get A Free Quote
BIM Construction is the Future
Building information modeling (BIM) is the future of building design and construction. Get in touch with our BIM Experts.