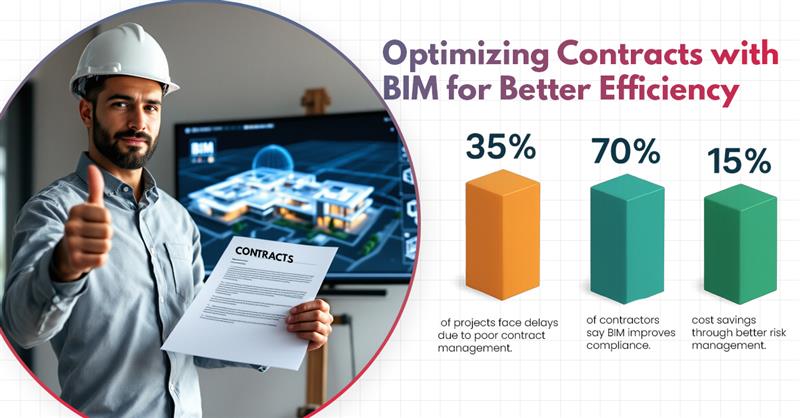
Risk management in construction faces major challenges that affect project success. Cost overruns plague construction projects due to underestimated original costs, unexpected challenges, and changes in project scope. Project delays increase expenses and leave stakeholders disappointed.
Table of Contents
ToggleBuilding Information Modeling (BIM) has become a vital tool to improve project efficiency. BIM offers a revolutionary solution by combining digital models, evidence-based decision-making, and shared live working in construction project management. Stakeholders can better control design changes, scheduling, budgeting, and risk assessment through 3D, 4D, and 5D BIM modeling.
BIM provides the quickest way to reduce risk in construction. Teams can spot where solids collide or clearances fall short as they detect clashes in BIM’s 3D virtual environment. BIM helps prevent scope creep, a common issue in the construction industry that leads to cost overruns.
This piece shows you how to optimize your construction contracts with BIM for live tracking, compliance monitoring, and complete risk management. Your projects will be more efficient and have fewer complications.
Contractual Clarity Through BIM Execution Plans
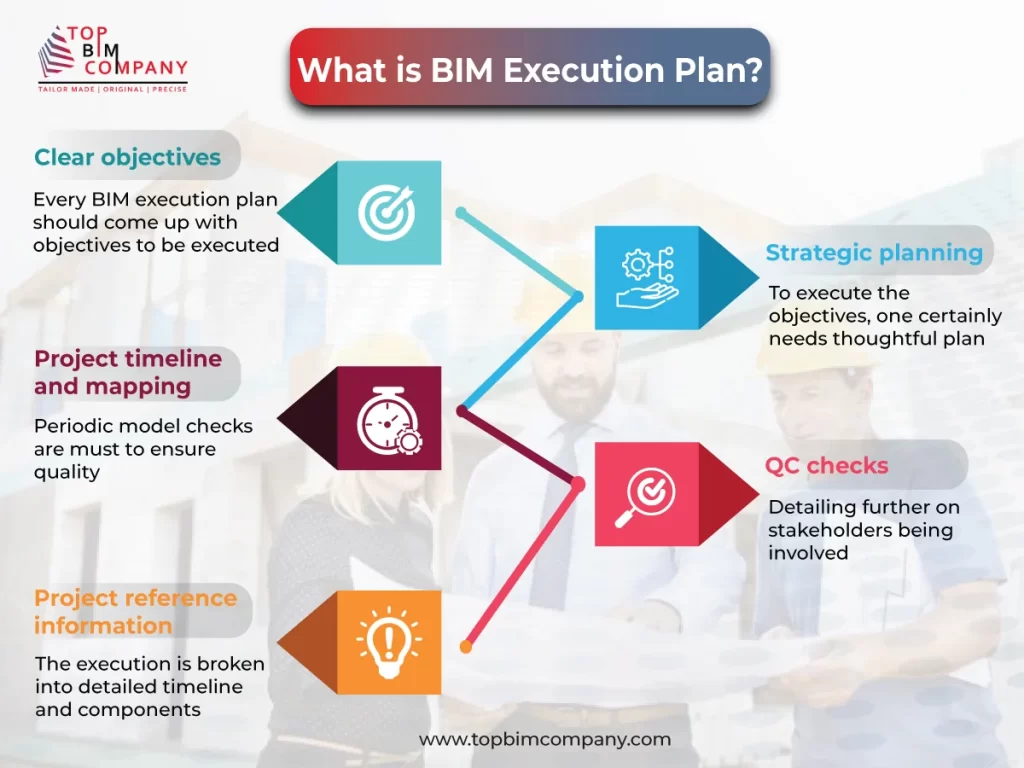
Construction contracts need clear protocols for digital collaboration. BIM Execution Plans (BIMxP) create a well-laid-out framework to manage project risks throughout the construction lifecycle.
What is a BIM Execution Plan (BIMXP)?
A BIM Execution Plan is a key planning document that outlines the implementation strategy for BIM on a project. The BIMxP acts as a “living document” that grows with the project lifecycle. Project teams use it to streamline information management and set clear expectations for all stakeholders.
The BIMxP details critical elements including:
- Model usage scope and extent
- Electronic collaboration procedures
- File naming conventions and software requirements
- Quality management protocols for model creation and validation
Industry standards show that a strong BIMxP helps teams communicate strategic goals, understand organizational roles, and set measures to track progress.
Defining roles and responsibilities in BIM contracts
Clear role definitions prevent responsibility gaps that can create construction risks. The BIMxP should outline BIM-related responsibilities for all project stakeholders. Common roles include BIM Manager, Project Manager, Model Element Author, and Discipline BIM Lead, though organizations use different terms.
Contracts must define each role with:
- Role name and general description
- Information management responsibilities
- Contract requirements for the role
This approach to role definition creates accountability for model accuracy and reduces misunderstandings.
Level of Development (LOD) and model sharing protocols
The Level of Development framework offers a standard language to define model element reliability at different project stages. LOD specifications range from conceptual (LOD 100) to as-built (LOD 500). Each level shows increasing detail and accuracy.
Standard LOD classifications include:
- LOD 100: Simple shape and size for conceptual design
- LOD 200: Approximate quantities and locations for schematic design
- LOD 300: Specific geometric information for detailed design
- LOD 400: Fabrication-level detail
Teams can better manage expectations about model accuracy by specifying LOD requirements in contracts. This reduces disputes and improves collaboration throughout the construction process.
Start building a sustainable future today. Get free BIM consultation for your project.

Standardizing BIM Contracts for Legal Protection
Legal risk management through standardized contracts has become vital for BIM-enabled construction projects. Digital collaboration growth demands specific contract documents that define responsibilities and protect stakeholders.
AIA E201 and E202 BIM contract exhibits
The American Institute of Architects (AIA) created specialized documents that deal with BIM-related legal concerns.
- E201-2022 serves as an exhibit for project participants who use BIM. This document lets them agree on terms about model uses, sharing, and reliance.
- E201’s most important feature allows project participants to list specific model versions as Contract Documents. This ensures all stakeholders understand model reliance expectations clearly.
- E202-2022 works in a similar way but doesn’t allow model versions to be listed as Contract Documents. Both documents have provisions for insurance coverage specific to BIM and digital data risks. These provisions address critical risk management aspects in construction projects.
ConsensusDocs 301 BIM Addendum overview
ConsensusDocs 301 stands as the first globally recognized contract addendum created to manage BIM’s legal aspects in construction.
- The document’s release in 2008 and subsequent updates revolutionized the industry. This groundbreaking document eases concerns about legal risks during transitions from 2D to 3D modeling environments.
- The BIM Addendum proves that “there is actually less legal risk in moving from the 2-D world to the 3-D world” by offering a balanced framework for BIM-enabled projects.
- The addendum has a standardized BIM Execution Plan that outlines technology requirements. These requirements create strong BIM use throughout a structure’s lifecycle.
- The document also tackles critical issues like model ownership rights, intellectual property terms, and liability provisions.
Clarifying model ownership and liability
Traditional responsibility division in standard contracts doesn’t work well as BIM evolves. Model ownership questions create major challenges. Who owns the data rights? Can teams use model data in future projects? Contracts must address these fundamental issues.
The standardized documents protect all parties by:
- Making design deliverable models clear
- Defining contract document models
- Setting requirements to preserve original models
- Outlining allowed model re-use cases
- Creating indemnity agreements for post-project model use
Building owners usually keep the BIM model’s ownership. Architects might worry about taking responsibility for models that many others helped create. This creates a complex liability situation that needs careful contract handling.
Using BIM for Risk Allocation and Accountability
BIM works as a powerful tool that manages construction risks through its data-rich environment. BIM creates better accountability throughout the project lifecycle than traditional methods by providing a detailed digital record of all decisions and changes.
Tracking model changes and version control
Version control is a key part of BIM’s risk management capabilities. It offers multiple benefits like collaborative workflow support, model state preservation, and complete revision history maintenance. Construction projects need several discipline experts to develop multiple versions of BIM models at the same time and share them frequently. BIM allows a systematic approach to track these revisions, resolve conflicts, and make real-time collaboration possible.
Modern version control systems work naturally with BIM platforms to manage 3D models and associated data through:
- Centralized repositories that provide a single source of truth
- Detailed logs documenting who made changes and when
- Quick access to specific versions of a file or document.
Assigning risk responsibility through model data
BIM changes the relationships between parties and often blends their roles and responsibilities. Even with these changes, core responsibilities stay the same—whether teams issue designs as 2D documents or 3D electronic models. BIM’s extensive project data history creates a baseline to monitor and compare efficiency levels throughout the building’s life.
This detailed documentation helps make it clear who is responsible for specific elements. This reduces confusion when problems come up. The model updates automatically for all project participants when changes occur. This substantially reduces potential clashes between project elements.
Reducing disputes with transparent model history
BIM systems’ transparency provides great benefits for dispute resolution. BIM documentation gives a complete overview of project progress. Teams can track design changes and find records of client decisions. The centralized data improves accountability and allows better decision-making throughout the project lifecycle.
Four-dimensional BIM adds time-based information to models. This helps resolve construction disputes about scheduling or delays. Better collaboration and communication through this transparency ended up reducing the likelihood of disputes.
Real-Time Data for Performance and Compliance Monitoring
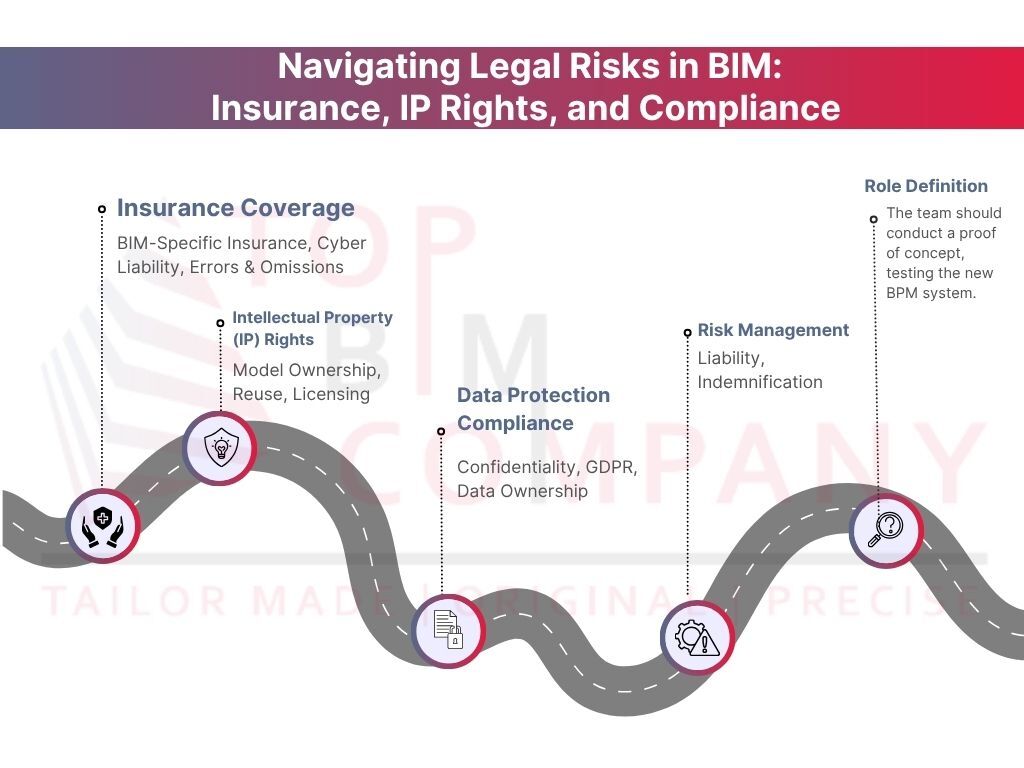
Live data collection is a vital step forward in construction risk management. Project teams can spot potential problems early through continuous monitoring systems before they turn into expensive fixes.
Integrating IoT and sensors with BIM for live updates
The Internet of Things (IoT) creates a network of electronic devices that gather and share live data in construction environments. Cloud-based platforms like ‘ThingsBoard’ connect wireless sensors that measure temperature, humidity, occupancy, and energy use to BIM models. Z-Wave standard sensors stand out with their low power needs, battery options, and range that covers about 100 meters.
Sensors on construction sites monitor concrete curing, weather patterns, and structural health. This data flows straight into BIM models for quick analysis. Project managers can then adjust their work plans and resources as needed to stay on schedule and within budget.
Using BIM dashboards for compliance tracking
BIM dashboards give teams a central view of project metrics, daily priorities, and risk factors. Teams can set up custom views that show relevant information to each project member.
Project dashboards show quick performance snapshots, while account-level views help analyze multiple projects for better business choices. These visual tools help teams check project health with current data and clear graphics. Teams can spot schedule risks and find specific issues before they delay the project.
Predictive analytics for future risk identification
Predictive analytics uses current and past data with statistical models and machine learning to forecast outcomes. Construction teams use these tools to decide on project bids, check if subcontractor prices make sense, and spot potential project troubles early.
The results speak for themselves. BAM Ireland saw their on-site quality and safety improve by 20%. Their staff spent 25% more time handling high-risk issues after they started using Construction IQ. Building Radar clients boosted their profits by 20% by using predictive models to shape projects in their early stages.
These prediction tools make job sites safer by studying past incidents and related factors. Construction teams can better understand what causes safety problems and create more effective prevention plans.
Conclusion:
This piece explores how BIM revolutionizes construction contract management and creates substantial advantages for project stakeholders. BIM execution plans create clear protocols that define roles, responsibilities, and model development expectations. Standard documents like AIA E201/E202 and ConsensusDocs 301 are the foundations of legal frameworks that protect all parties in BIM-enabled projects.
BIM’s data-rich environment provides unprecedented accountability through detailed tracking of changes and version control. Teams can trace decisions back to their source and clearly establish responsibility, which reduces disputes substantially. It also enables immediate monitoring through IoT integration and sensors that feed live data directly into models. You can address issues before they get pricey.
BIM’s predictive capabilities help you spot potential risks before they surface. Companies using these technologies report better quality, safety, and profitability. Preventing problems is nowhere near as expensive as fixing them later.
BIM marks a transformation from reactive to proactive construction management. Traditional methods often leave teams scrambling to fix unexpected issues. BIM gives you the tools and data to anticipate challenges. Complex construction projects make BIM essential to work effectively.
Your project’s success depends on being willing to adopt these digital tools fully. Setting up detailed BIM protocols needs original investment and organizational change. The improvements in project outcomes make it worth the effort. Teams that become skilled at BIM implementation gain a competitive edge. They deliver projects with fewer complications, better efficiency, and happier clients.
Further Reading
BIM for Sustainability and Energy Efficiency Modeling
Building Information Modeling for Infrastructure : Comprehensive Guide
Comparison of BIM Modeling in Various Typologies
Competitive Advantages Of BIM Automation In The AEC Industry
BIM for Heritage Preservation – Future of Protecting Our Past
Future-Proofing AEC Projects: The Role of BIM in Meeting Both ADA and OSHA Standards
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs):
BIM defines data deliverables, responsibilities, and coordination workflows to align stakeholders to contractual expectations.
By providing a clear digital record and accountability for model updates and deliverables.
Yes, deliverables such as LOD targets, coordination models, and clash reports ensure clear expectations.
Miscommunication, data gaps, and scope ambiguity are reduced with BIM’s structured data requirements.
They become annexures that outline roles, tools, timelines, and data responsibilities agreed by all parties.
Our Services
Latest Post
Get A Free Quote
BIM Construction is the Future
Building information modeling (BIM) is the future of building design and construction. Get in touch with our BIM Experts.





