As the world ventures into an era dominated by technology, its impact has reached every nook and cranny of various industries, and the construction sector is no exception. One notable transformation has been the digitization of processes that were once manual and time-consuming. One such crucial aspect is as-built documentation.
Table of Contents
ToggleThis blog delves into the significance of as-built documentation, the challenges posed by traditional methods, and how digitization has revolutionized this aspect of the construction industry.
Also Read: BIM Integrated As-Built Drawings for Building Construction Management
The Importance of As-Built Documentation
As-built documentation refers to the accurate representation of a construction project after its completion. It includes detailed drawings, measurements, and information about the final state of the project.
This documentation is invaluable as it serves as a reference for maintenance, renovations, and future developments.
Would Like to explore As Built Drawing Services
Without accurate as-built documentation, making changes or improvements to a structure becomes an arduous task, often resulting in errors, delays, and increased costs.
Challenges in Traditional As-Built Documentation
In the traditional construction landscape, creating as-built documentation was a cumbersome process. Manual measurements, handwritten notes, and physical drawings were prone to errors, inaccuracies, and misinterpretations.
This led to discrepancies between the planned design and the actual construction, causing confusion and inefficiencies during maintenance or renovations.
Additionally, locating and retrieving physical documents when needed could be time-consuming, hindering timely decision-making.
Role of Digitization in As-Built Documentation
Digitization has emerged as a game-changer in the field of as-built documentation. By leveraging digital tools and technologies, the construction industry can address the shortcomings of traditional methods and unlock numerous benefits.
- Accurate Data Capture: Digitization allows for precise data capture through methods like laser scanning and Photogrammetry. These techniques enable the creation of detailed and accurate digital representations of the built environment. Laser scanning captures millions of data points in seconds, creating a highly accurate 3D model. This enhanced accuracy translates into more reliable as-built documentation, reducing errors and discrepancies. Moreover, digitization doesn’t stop at mere data capture. It leads to enhanced visualization, allowing stakeholders to virtually explore the structure, identify potential issues, and plan modifications before they are implemented.
Digital Tools for As-Built Documentation: Sequential Approach to Digitized Accuracy
Laser Scanning/Photogrammetry:
The journey into digitized as-built documentation often begins with laser scanning and Photogrammetry. These technologies provide the foundation for a precise digital representation of the built environment.
Laser scanning rapidly captures an extensive array of data points, constructing a comprehensive 3D model. Photogrammetry, on the other hand, utilizes photographs to create accurate measurements and models.
Software: Leica Cyclone and Autodesk ReCap:
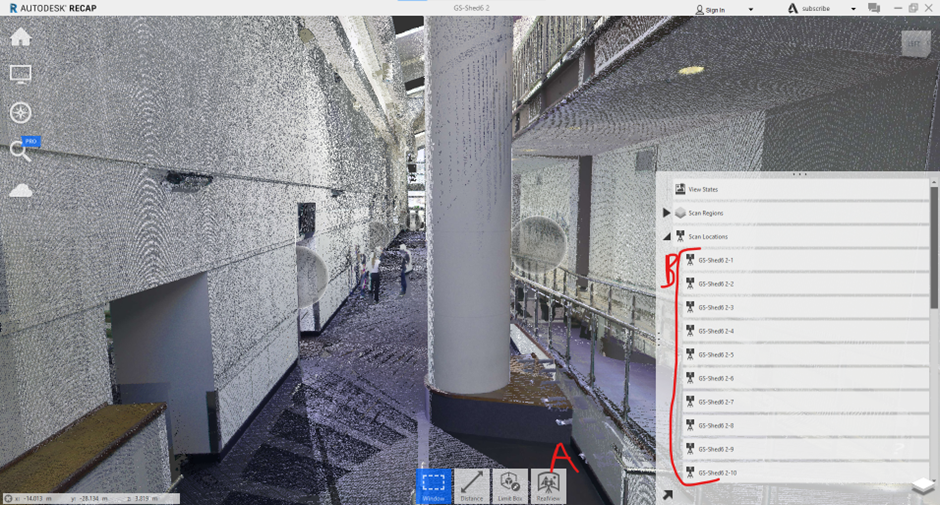
Process:
Laser Scanning: Leica Cyclone is a software commonly used for processing laser scan data. It takes data collected from laser scanners, which emit laser beams to capture the geometry of objects and environments. These scanners capture millions of data points, creating a detailed point cloud representing the as-built environment.
Photogrammetry: Autodesk ReCap employs photogrammetry to process images taken from various angles. These images are analyzed to create a 3D model by triangulating points from different images, allowing accurate measurements and models to be generated.
Building Information Modeling (BIM):
Building Information Modeling, or BIM, is the cornerstone of modern construction documentation. It involves the creation of a collaborative 3D model that integrates information from multiple sources, offering a holistic view of the project. BIM captures the physical aspects of the structure but also includes data related to materials, costs, schedules, and more. This integration of diverse information streamlines updates, revisions, and maintenance procedures.
Software: Autodesk Revit
Process:
Creating a Collaborative Model: In Autodesk Revit, architects, engineers, and other stakeholders collaborate to create a shared 3D BIM model. This model includes not only the geometry of the building but also information about materials, systems, and schedules.
Integration of Data: BIM software like Revit allows importing data from laser scanning and photogrammetry. This data can be used to create an accurate starting point for the BIM model.
Integration of IoT Data with BIM for As-Built Documentation:
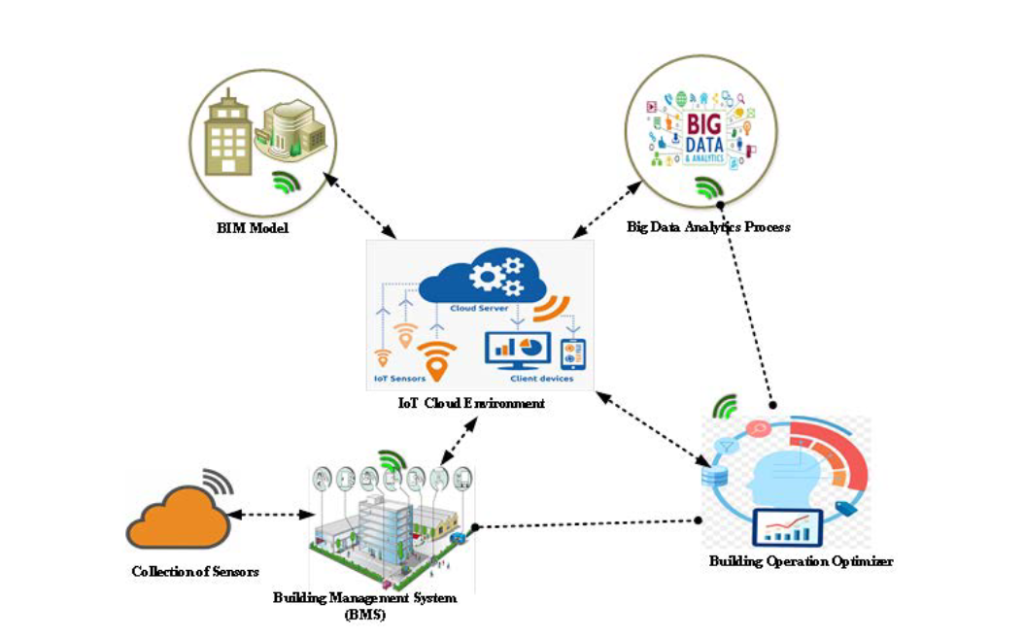
The integration of Internet of Things (IoT) data with BIM marks the next step in the digitized as-built approach. IoT devices embedded within the structure, such as sensors and smart components, gather real-time data on various parameters like temperature, humidity, structural integrity, and energy consumption.
This continuous data flow enhances as-built documentation by providing insights into the structure’s performance over time. It equips maintenance teams with the ability to monitor the health of the building and address issues proactively.
Software: Autodesk BIM 360 and IoT Platforms
Process:
IoT Data Collection: Sensors and smart devices embedded within the structure collect real-time data on factors like temperature, humidity, energy usage, and structural health.
Integration with BIM: Platforms like Autodesk BIM 360 enable the integration of IoT data with the BIM model. This data is visualized within the model, providing a real-time view of the building’s performance.
Benefits of Digitized As-Built Documentation
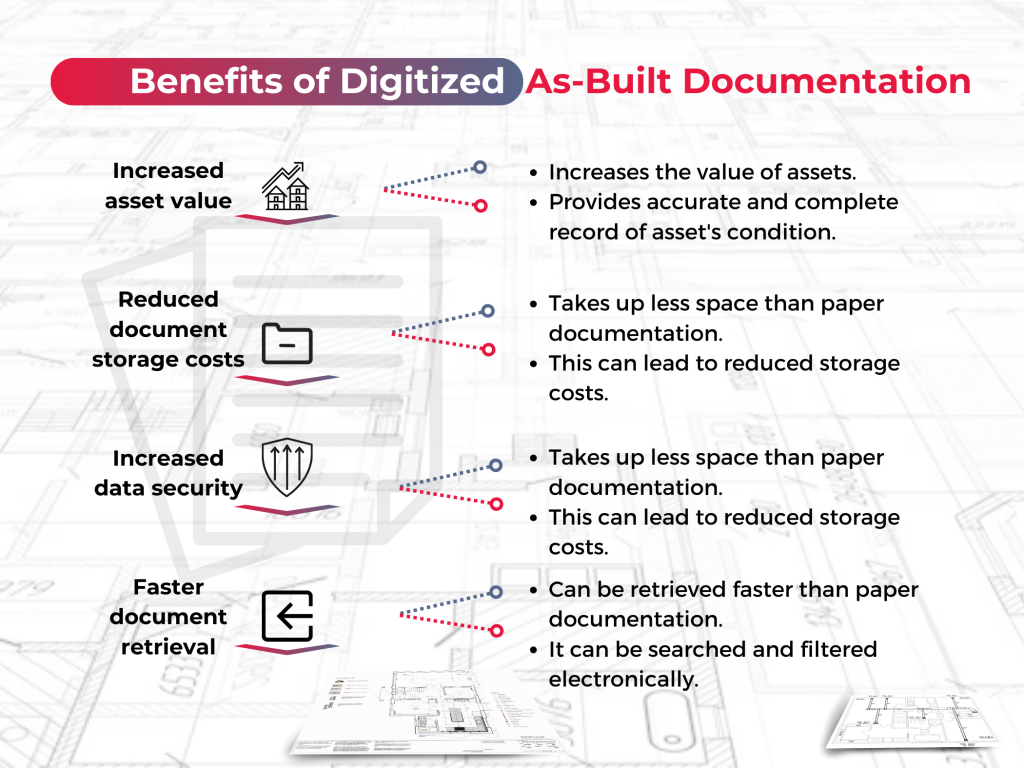
- Accuracy and Precision: Digitization minimizes human errors and ensures that as-built documentation accurately reflects the physical reality.
- Efficiency: Digital tools expedite the process of capturing and updating information, saving time and resources.
- Cost Savings: Accurate documentation reduces the likelihood of errors during renovations or modifications, saving money in the long run.
- Collaboration: Digitized documentation can be easily shared among stakeholders, fostering better collaboration and informed decision-making.
Best Practices for Implementing Digitization in As-Built Documentation
- Training: Provide training to construction professionals on using digital tools effectively.
- Data Management: Establish a structured system for organizing and storing digital documentation.
- Regular Update: Schedule regular updates to ensure that digital documentation remains current and relevant.
Overcoming Challenges and Considerations
While digitization offers substantial benefits, challenges such as initial investment costs, data security, and the learning curve must be addressed. Construction companies should carefully evaluate their needs, choose appropriate digital tools, and ensure a smooth transition from traditional methods to digital workflows.
Challenging Traditional As-Built Drawings with 3D Scans:
Traditional as-built drawings often fall short in accuracy and reliability, leading to unexpected hurdles and costly delays. Enter 3D as-built scans, capturing every inch with millimeter precision. From design simulations to operational insights, everything happens digitally.
- Overcoming 2D Complexity: 2D as-builts can confuse the best of us. 3D scans create digital environments, understood from the boardroom to the factory floor. The interactive 3D view simplifies communication, enhancing remote collaboration.
- Swift and Smart Generation: Generating as-builts usually takes ages. 3D scans? Sometimes a quick lunch break suffices. Review later. For project risk management, scan daily to stay on top of every project facet.
- Banishing On-Site Rework: Changes equal more measurements. Not with 3D scans. Accurate measurements anytime, anywhere, even in tight corners. Plan, rework, or tweak without setting foot on-site.
- Streamlining Retrofit Challenges: 2D makes retrofits tricky. 3D scans ease equipment planning, clash detection, and risk management. Visualize movement and placements, reducing delays.
- Seamless Update: New gear and changes in 2D? Messy. 3D scans clean up. Post-project, swift and exact 3D scans cover updates, insurance records, and design references.
- Tackling Fitment Fiascos: Misfit gear and faulty designs? Bye-bye, with 3D scans. Clash detection and fab validation in 3D ensure equipment’s spot-on, saving time and resources.
3D Scans: The Game-Changer
When it’s about documentation, 3D laser scans rock. The quickest, most precise, and efficient way. Tons saved by spotting even a single glitch. Skilled 3D scanning partners? Priceless. It’s the ticket to on-budget, on-time projects.
For architects, engineers, and more, 3D scans gift the power of foresight. Say goodbye to budget overruns and delays. Embrace the future of as-built documentation and project analysis.
Elevating As-Built Drawing Standards with PlanRadar Software
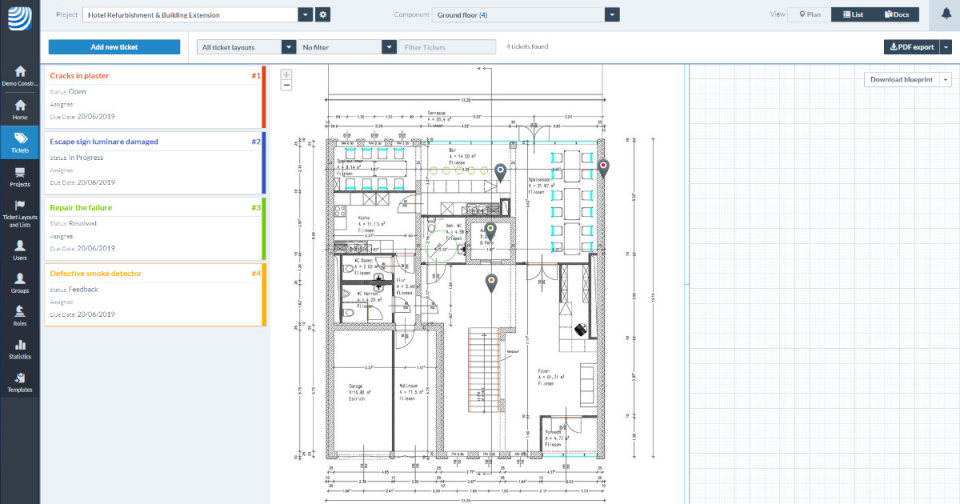
- Seamless Versioning: PlanRadar simplifies version management by enabling easy upload and comparison of multiple building plan iterations. This streamlined approach tracks changes over time, ensuring a comprehensive view of the project’s evolution.
- Precise Time and Location Stamps: Every change made to the original plan is automatically time, date, and location stamped. This feature offers clarity to future teams, pinpointing the exact site and time of alterations.
- Clear and Detailed Notes: Gone are handwritten notes. PlanRadar allows detailed notes and changes to be recorded using typed text within the app. Voice recordings can also be stored for additional context.
- Visual Documentation: Photographs play a crucial role. PlanRadar permits capturing and logging changes through images, aiding future workers in understanding past modifications.
- Secure Cloud Storage: Digital as-built drawings find a secure home in the cloud. This ensures changes are preserved without the risk of misplacement or disposal.
Conclusion:
The construction industry’s adoption of digitization for as-built documentation marks a pivotal step towards a more efficient, accurate, and collaborative future. The combination of precise data capture, advanced visualization, and streamlined updates transforms as-built documentation from a time-consuming chore into a strategic advantage. By embracing digitization, the construction sector can build a solid foundation for future growth and innovation.You may also like to read:
- 3D Scanning Software Apps & Technologies in Construction Industry
Best GIS Mapping Softwares for Construction Industry
Autodesk BIM Batch Suite 2024 | New Features & Benefits - BIM Management- Building Construction Process For General Contractors
- 4 Stages of BIM Process in Building Construction
- Benefits and Role of BIM Design in Construction
- BIM Integrated As-Built Drawings for Building Construction Management
- 5 Ways of Improving the Value of BIM Objects

Want to know more about the benefits of BIM in facility management
Contact TopBIM consultants at preconstruction!
Our Services
Latest Post
Get A Free Quote
BIM Construction is the Future
Building information modeling (BIM) is the future of building design and construction. Get in touch with our BIM Experts.